-
赋存于变质地体中的脉状金矿床,是全球最重要的热液金矿床类型之一,查明成矿系统Au和S的来源,一直是金矿床研究的核心科学问题(Goldfarb et al., 2023)。由于金矿床的赋矿围岩复杂多样,导致赋矿围岩对成矿的贡献长期存在争议,如西澳太古代造山型金矿床形成于围岩变质脱挥发分过程,暗示成矿物质和流体主要来自赋矿围岩(Phillips et al., 2010)。然而,对于成矿时代明显晚于围岩的脉状金矿床,如中国胶东最大的金成矿省,赋矿围岩为成矿系统提供金的可能性不大(邓军等,2023),但赋矿围岩对成矿系统硫的贡献目前仍存在不同认识(Qiu et al., 2023)。Large等(2007)对Sukhoi Log超大型金矿床赋矿围岩(黑色页岩和粉砂岩)中沉积-成岩期的黄铁矿进行了激光原位微量元素分析,发现这些黄铁矿中的不可见w(Au)高达12×10-6,提出赋矿围岩是成矿系统金的主要来源。中低温热液金成矿体系中,S作为Au运移的最主要络阴离子,Au(HS)2-、Au(HS)0、HAu(HS)20作为Au的主要运移形式(Pokrovski et al., 2013),故厘定赋矿围岩对成矿系统S和Au的贡献,是揭示矿床成因的关键。
江南造山带是中国最重要的黄金产区之一,以广泛分布于前寒武系板岩中的脉状金矿床为特色,累计探明金储量约970 t(毛景文等,1997; Xu et al., 2017; Li et al., 2023)。马东升等(2002)基于传统粉末法分析获得湘中地区冷家溪群和板溪群w(Au)分别为3.6×10-9和3.1×10-9,是上部大陆地壳w(Au)的1.6~8.6倍,同时根据矿区蚀变围岩中的w(Au)普遍低于周围未蚀变岩石和区域地层背景值,提出赋矿围岩为矿源层。最新全岩地球化学和激光原位微量元素分析结果显示,赋矿板溪群及其沉积黄铁矿的w(Au)多<1×10-9,且沉积黄铁矿的δ34S值(+15.6‰~+25.8‰)明显不同于古台山、玉横塘等金矿床中热液毒砂和黄铁矿的δ34S值(多集中在0±5‰),结合成矿年代学等证据,学者提出这些板岩中的脉状金矿床的形成与岩浆作用密切相关,赋矿围岩不是Au和S的主要来源(Li et al., 2019;2023)。因此,开展江南造山带不同区带赋矿围岩对成矿作用的贡献,是深化区域金矿成矿机制的关键。
湘东北矿集区位于江南造山带中部,发育万古和黄金洞等大型金矿床(图1,董国军等,2008;Xu et al., 2017),矿床成因仍存在争议。前人基于全岩地球化学分析结果,提出冷家溪群为矿源层(罗献林,1990;刘英俊等, 1991;Zhang et al., 2020)。部分学者认为赋矿地层和燕山期岩浆热液共同提供成矿物质(毛景文等,1997),也有学者提出这些金矿床的形成与深部岩浆作用密切相关,燕山期构造活化诱发深部流体向浅部运移富集成矿(Xu et al., 2017;Deng et al., 2020)。传统粉末法和激光原位S同位素分析结果显示,黄金洞和万古等金矿床中的热液黄铁矿和毒砂的δ34S值主要分布在-14.2‰~-0.5‰(夏浩东等,2017;刘育等,2017;Zhang et al., 2018;李荣华等, 2020),明显不同于岩浆S同位素组成(δ34S= 0±5‰;Ohmoto, 1986),因此,进一步查明成矿系统中S和Au的来源,是限定矿床成因的重要内容。
本次研究聚焦黄金洞大型金矿床,以赋矿板岩中的沉积黄铁矿为研究对象,通过对其开展钻孔编录、岩相学和激光原位微区元素和硫同位素分析,查明赋矿围岩对成矿作用的贡献,为厘定矿床成因提供新约束。
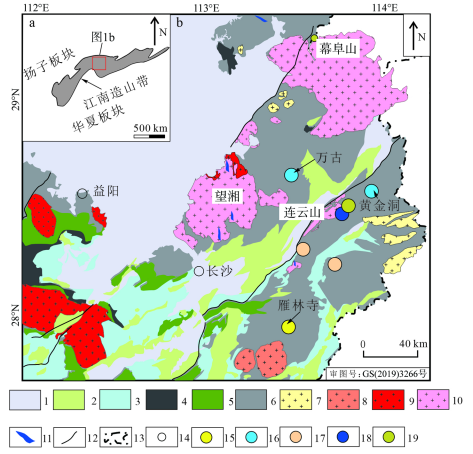
1区域地质背景江南造山带又称为江南古陆,是华南重要的金成矿带之一,是扬子板块与华夏板块新元古代碰撞结合的产物(毛景文等,1997; Greentree et al., 2006; Xu et al., 2017)。江南造山带中部湖南段金矿床数量最多、金资源储量/资源量最大(黄建中等,2020),包括万古、黄金洞、沃溪等大型金矿床。江南造山带以发育上元古界变质基底为特征,构成了区域特色的双层地层结构:上元古界变质岩基底和古生界至新生界沉积盖层(湖南省地质矿产局,1988),包括新元古代冷家溪群和板溪群、二叠系和白垩系(毛景文等,1997)。新元古代冷家溪群和板溪群岩性主要为浅灰色-浅灰绿色绢云母板岩和绿泥石板岩,且普遍发育沉积黄铁矿(Li et al., 2019;2021)。
湘东北地区位于江南造山带的中部(图1a),构造主要由近东西向-北西(西)向韧性剪切带、一系列次级断裂和北东向断裂和褶皱组成(图1b,文志林等,2016;Zhou et al., 2021)。湘东北地区主要发育有3条断裂,自西向东分别是新宁-灰汤断裂、长沙-平江断裂和醴陵-衡东断裂,断裂走向均为NNE向。其中长沙-平江断裂控制了万古、黄金洞等矿床的分布。根据断裂带两侧的运动学标志和应力分析,长沙-平江断裂带经历了新元古代、加里东期、印支期、燕山期多期走滑和拉伸(Zhou et al., 2021)。湘东北地区岩浆岩发育,成岩时代包括新元古代、加里东期、印支期和燕山期(图1b),以分布在黄金洞、万古金矿床周缘的燕山期花岗岩规模最大。
2矿床地质特征黄金洞金矿床位于湖南省岳阳市平江县,其累计探明金储量约80 t,平均品位5 g/t(Zhang et al., 2018),达到大型规模,其矿体由杨山庄、金塘、华家湾、金福和金枚5个矿段组成,这些矿段均位于长沙-平江断裂下盘(图2a)。矿区内无岩浆岩出露,仅在东南方向分布有燕山期连云山花岗岩,锆石U-Pb年龄限定其成岩时代为150~140 Ma(许德如等,2017;Deng et al., 2017)。
图1江南造山带中湘东北地区构造位置图(a)及其主要金属矿床和岩体分布图(b,据Li et al., 2023修改)1—新生界泥岩、砾岩和黏土岩;2—中生界碳酸盐岩、页岩和砂岩;3—古生界页岩、砂岩和白云岩;4—上元古界南华群/震旦系板岩、砾岩和粉砂岩;5—上元古界板溪群板岩、粉砂岩和泥质岩;6—上元古界冷家溪群板岩、变质砂岩和粉砂岩;7—新元古代花岗岩;8—志留纪花岗岩;9—三叠纪花岗岩;10—晚侏罗世—白垩纪花岗岩;11—煌斑岩;12—断层;13—省界;14—城市;15—Au矿床;16—Au-W矿床;17—Cu-Pb-Zn矿床;18—W-Sn矿床;19—Be-Nb-Ta-Li矿床
Fig. 1 The tectonic location map (a) of the northeastern Hunan in Jiangnan orogenic belt and its geological map showing main types of mineral deposits and intrusions (b, modified after Li et al., 2023)
1—Cenozoic mudstone, conglomerate and clay rock; 2—Mesozoic carbonate rock, shale and sandstone; 3—Paleozoic shale, sandstone and dolomite; 4—Upper Proterozoic Nanhua Group/Sinian slate, conglomerate and siltstone; 5—Neoproterozoic Banxi Group slate, siltstone and argillaceous rocks; 6—Neoproterozoic Lengjiaxi Group slate, metasandstone and siltstone; 7—Neoproterozoic granite; 8—Silurian granite; 9—Triassic
granite; 10—Upper Jurassic—Cretaceous granite; 11—Lamprophyre;12—Fault; 13—Provincial boundaries; 14—City; 15—Au deposit; 16—Au-W deposit; 17—Cu-Pb-Zn deposit; 18—W-Sn deposit; 19—Be-Nb-Ta-Li deposit
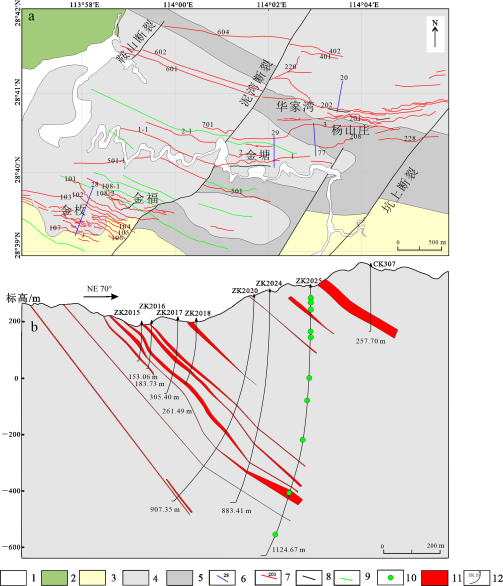
图2黄金洞金矿床平面地质图(a)及简化地质剖面图(b)1—第四系;2—白垩系戴家坪组;3—冷家溪群第三岩组第二岩性段;4—冷家溪群第四岩组第二岩性段;5—冷家溪群第四岩组第一岩性段;
6—岩体和编号;7—勘探线及编号;8—断裂;9—倒转背斜;10—采样位置;11—矿体;12—钻孔及其编号
Fig. 2 Geological map (a) and simplified geologic cross section (b) of the Huangjindong gold deposit 1—Quaternary System; 2—Cretaceous Daijiaping Formation; 3—The Second lithologic segment of the Third rock Formation of Lengjiaxi Group;4—The Second lithologic segment of the Fourth rock Formation of Lengjiaxi Group; 5—The First lithologic section of the Fourth rock Formation of Lengjiaxi Group; 6—Rock mass and number; 7—Exploratory line and number; 8—Fault; 9—Overturned anticline; 10—Sample location;11—Orebodies; 12—Drill holes and their numbers
黄金洞金矿床赋矿围岩为新元古代冷家溪群坪原组,主要由呈青灰色-黄绿色粉砂质板岩、绢云母板岩和变质细砂岩组成,形成于深海-半深海环境,发育沉积黄铁矿(唐晓珊,1989)。在矿区的西北部出露见白垩系红层(图2b)。
矿区褶皱和断裂发育,褶皱主要为倒转背向斜,褶皱枢纽走向北西(西)。矿区发育2组断裂,分别为EW-NWW向和NE-SW向,倾角通常大于50°。矿脉主要产于EW-NWW向断裂破碎带中,在空间上平行成群展布,多数倾向北,倾角40°~75°,少数倾向南,倾角60°~75°。北东向断裂主要为泥湾断裂和许多近平行的次级断裂,与成矿作用的关系有待查明。
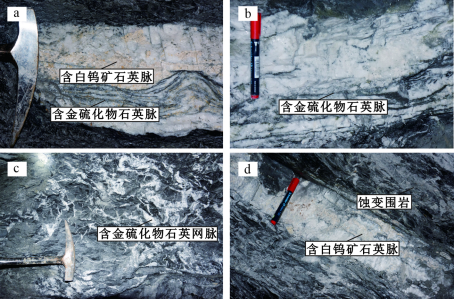
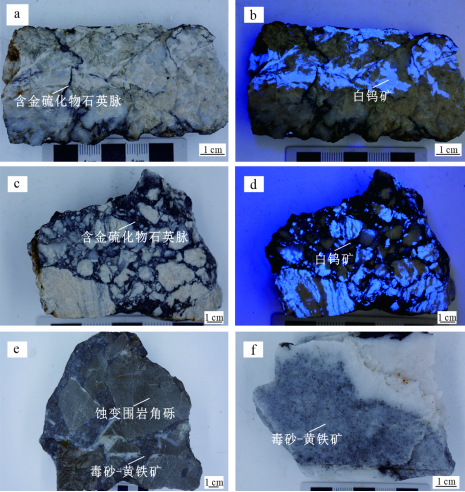
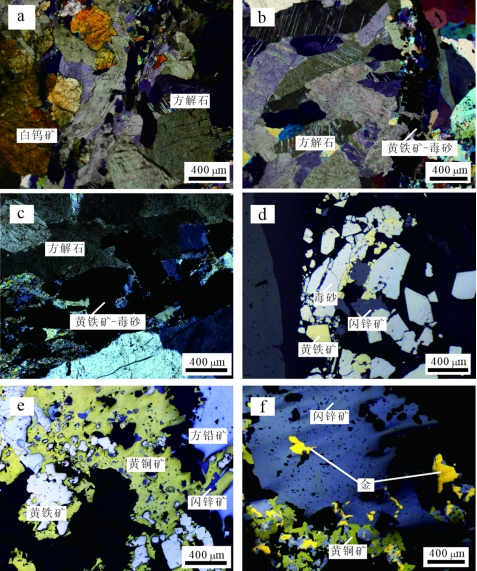
黄金洞矿床矿体呈脉状、透镜状、扁豆状分布,具膨胀、收缩、尖灭的特点,主要由含金石英脉、含金石英网脉和含金蚀变板岩组成(图3a~d),矿石类型主要为石英脉型和蚀变岩型,少量为构造角砾岩型(图4a~f)。规模最大的1号脉和3号脉的金资源量占整个矿区金资源量的50%以上(周岳强等,2021)。1号脉走向延伸长约3200 m,矿体厚0.46~2.16 m,倾向北;3号脉走向延伸长约3300 m,矿体厚0.74~3.65 m,倾向南。矿石矿物主要为毒砂、黄铁矿和自然金,脉石矿物主要为石英、白钨矿、方铅矿、闪锌矿、黄铜矿、方解石、绿泥石、绢云母等(图5a~f)。石英脉中白钨矿呈角砾被含金硫化物细脉胶结(图4c、d),暗示白钨矿早于载金硫化物沉淀(Deng et al., 2020)。
围岩蚀变是重要的找矿标志之一,主要发育在石英脉两侧破碎板岩中,颜色特征主要表现为灰绿色板岩,褪色为浅黄色。TESCAN综合矿物分析仪(TIMA)和微区X射线荧光光谱分析(μ-XRF)分析显示,褪色化蚀变带中主要发生碳酸盐化、绢云母化和硅化(Zhang et al., 2018;许可等,2022)。褪色化蚀变带中分布浸染状的毒砂和黄铁矿。
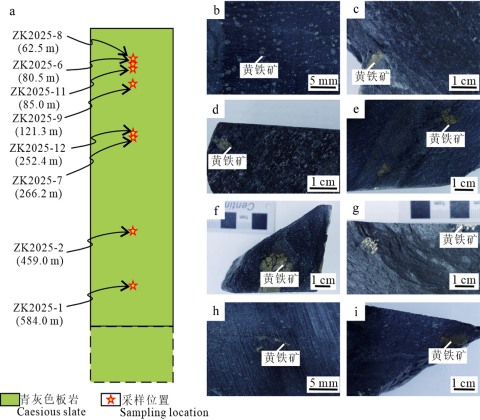
3样品特征及分析方法3.1样品特征本次工作收集整理已有钻孔资料,选取金枚矿段20号勘探线的ZK2025钻孔进行了编录,样品位置信息如图6 a所示,采集样品深度分别为62.5 m、80.5 m、85.0 m、121.3 m、252.4 m、266.2 m、459.0 m、584.0 m,对应样品编号为ZK2025-8、ZK2025-6、ZK2025-11、ZK2025-9、ZK2025-12、ZK2025-7、ZK2025-2、ZK2025-1。沉积黄铁矿手标本主要呈团块集合体状,62.5 m、584.0 m位置的沉积黄铁矿手标本呈星点状分布(图6a~g)。
图3黄金洞金矿床典型含金脉体特征 a.石英脉型矿体,早期含白钨矿石英脉被晚期含金硫化物石英脉切穿;b.多条近平行分布的含毒砂-黄铁矿的石英细脉充填在早期石英脉中;c.围岩呈角砾被含金石英网脉充填;d.灰黑色蚀变围岩中的含金硫化物石英脉,围岩中发育硫化物
Fig. 3 Photographs showing characteristics of the typical ore-bearing orebodies from the Huangjindong gold deposit a. Quartz vein, early scheelite quartz veins cut through late gold sulfide quartz veins; b. Quartz veins containing multiple near-parallel distribution of arsenopyrite-pyrite within early quartz veins; c. The wall rock breccia filled with gold-bearing quartz veins; d. Gold sulfide quartz vein in gray-black alteration surrounding rock, and sulfide developed in surrounding rock
图4黄金洞金矿床不同类型矿石手标本照片 a、b.石英脉型矿石,毒砂和黄铁矿主要分布在含金硫化物中。早期含白钨矿石英脉被晚期含金硫化物石英脉切穿,白钨矿在紫外灯照射下呈天蓝色;c、d.石英脉型矿石,早期的含白钨矿的石英呈角砾状被晚期的含金硫化物石英脉切穿,白钨矿在紫外灯照射下呈天蓝色;e.石英脉型矿石,围岩呈角砾状被含金硫化物石英胶结;f.石英脉型矿石,早期的白色石英被晚期含有浸染状硫化物的烟灰色石英切穿
Fig. 4 Photos of different types of ore hand samples in Huangjindong gold deposit
a, b. Quartz vein-type ore, arsenopyrite and pyrite are mainly distributed in gold-bearing sulfide. Early scheelite quartz veins are cut by late gold sulfide quartz veins, scheelite appears sky blue under ultraviolet light; c, d. Quartz vein-type ore, Early scheelite quartz is brecciated by late gold sulfide quartz veins, scheelite appears sky blue under ultraviolet light; e. Quartz vein-type ore, The surrounding rock is brecciated by gold sulfide quartz;
f. Quartz vein-type ore, early clean quartz is cut through by later smokey gray quartz containing disseminated sulfide
3.2测试分析方法电子探针测试分析在中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所电子探针实验室完成。实验仪器型号为JXA-8230,实验条件为加速电压20 kV,电流20 nA。黄铁矿激光剥蚀等离子体质谱(LA-ICP-MS)微区原位微量元素含量测试分析在广州市拓岩检测技术有限公司完成。实验室采用New Wave Research 193nm ArF准分子激光剥蚀系统,与Thermo Scientific iCap-RQ四极杆型电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICP-MS)联用。激光束斑直径为30 µm,频率为6 Hz,能量密度为3.5 J/cm2。微区原位微量元素含量测试和处理过程中采用玻璃标准物质NIST SRM610和MASS-1进行多外标无内标校正(Liu et al., 2008),采用比例标准物质SRM612和BCR-2Ga作为监控样品。每个时间分辨分析数据包括大约40 s空白信号和45 s样品信号,数据的离线处理采用软件Iolite完成。黄铁矿LA-MC-ICP-MS原位S同位素测试在中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所完成。仪器由Resonetics-S155 ArF准分子激光剥蚀系统和Neptune Plus MC-ICP-MS组成。能量密度为5.0 J/cm2,束斑直径为32μm,频率为6 Hz。以氦气作为载气。测试过程中使用的数据校正方法为“标准-样品-标准”交叉测试(SSB),每测1个样品前后各测1次标样。本实验以黄铁矿(JX,δ34SV-CDT=16.9±0.5‰)作为标样。元素能谱分析在自然资源部战略性金属矿产找矿理论与技术部重点实验室TIMA实验室完成,分析仪器为捷克泰思肯电镜公司(TESCAN)的自动矿物分析系统,仪器型号为TIMA-GMS。能谱分析仪器为美国EDAX公司的X射线能谱仪,型号为Element,处理软件为APEX,有效探测面积25 mm2,Mn、Ca分辨率优于129 eV,分析元素范围:Be4~Am95待测样品在实验前进行喷碳,将需要测试的样品用导电胶粘贴在样品台上。在真空模式下,设置加速电压为25 keV,电流为300 pA,工作距离为15 mm。
图5黄金洞金矿床不同类型矿石矿物组成显微照片 a.含白钨矿的石英脉与方解石共生;b、c.方解石-石英脉被含毒砂、黄铁矿石英脉切穿;d.金矿石中的硫化物由毒砂、黄铁矿、闪锌矿组成;e.毒砂、黄铁矿、闪锌矿和方铅矿组成;f.自然金与黄铜矿、闪锌矿共生
Fig. 5 Photomicrograph showing the mineral assemblage of different ores from the Huangjindong gold deposit
a. Quartz veins containing scheelite are associated with calcite; b, c. Carbonate-quartz veins are crosscut by veins containing arsenopyrite and pyrite; d. The gold sulfide is composed of arsenopyrite, pyrite and sphalerite; e. The gold-bearing sulfide consists of arsenopyrite, pyrite, sphalerite and galena; f. The gold sulfide is composed of arsenopyrite, pyrite, sphalerite and native gold
图6黄金洞金矿床钻孔ZK2025取样位置示意图(a)及样品手标本照片(b~i)b、h.星点状黄铁矿;c~g、i.团块状黄铁矿集合体。
Fig. 6 Photographs showing the sample location and features of samples from the drillhole ZK2025 in Huangjindong Au deposit b, h. Star-spotted pyrite; c~g, i. Lumpy pyrite
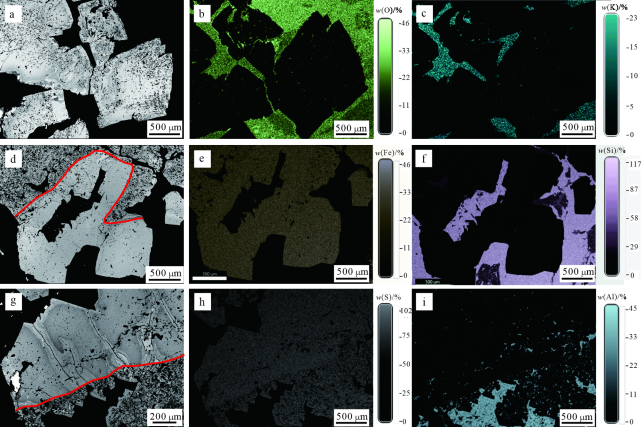
4分析结果4.1显微结构特征显微结构研究表明,板岩中的沉积黄铁矿呈半自形-他形粒状集合,粒径多为几百~几千μm(图7a~f)。沉积黄铁矿中见很多硅酸盐矿物包体,如绢云母。部分沉积黄铁矿经历成岩期和后期热液作用发育非均一结构,表现为沿黄铁矿颗粒间隙分布有后期热液蚀变边(图7g~i)。
4.2原位微区硫同位素沉积黄铁矿原位S同位素分析结果见表1。
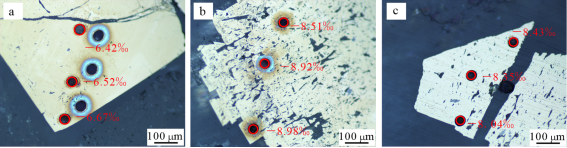
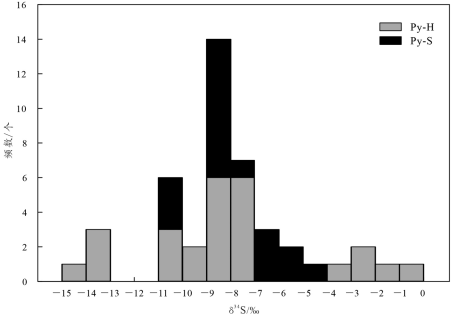
沉积黄铁矿硫同位素组成总体呈现同一样品的变化不大、不同样品之间存在一定的差异的变化特征(图8a~c),其δ34S值介于-10.9‰~-4.7‰(图9)。
4.3微量元素组成沉积黄铁矿开展系统的LA-ICP-MS元素含量分析,并对每一个LA-ICP-MS测试点的测试信号值随时间变化情况进行逐一核实,最大程度地避免矿物包体对元素含量的影响,并选取各信号峰最为平坦的信号时间区间计算其微量元素含量(图10a~f)。
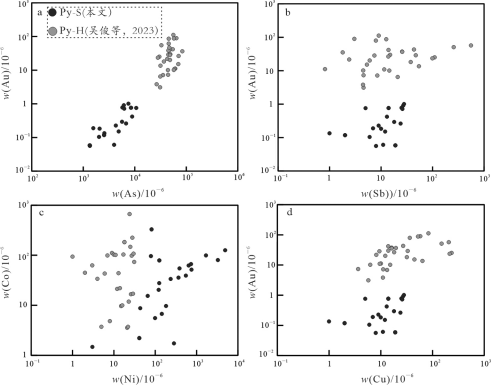
沉积黄铁矿LA-ICP-MS微量元素分析结果如表2所示。沉积黄铁矿中不可见w(Au) < 1.0×10-6;w(As)范围为795×10-6~10 666×10-6,平均为3770×10-6。除Au和As外,还含有一定量的Sb,含量介于1.5×10-6~63.8×10-6,平均为12.6×10-6。w(Co)、w(Ni)和w(Pb)平均为48.4×10-6、105×10-6和146×10-6(图11)。
图7黄金洞金矿床沉积黄铁矿电子探针显微结构和元素面扫描照片 a.自形-半自形黄铁矿集合体;b.氧元素面扫;c.钾元素面扫;d、g.半自形-他形沉积黄铁矿集合体,后期发生热液蚀变;e.铁元素面扫;f.硅元素面扫;h.硫元素面扫;i.铝元素面扫
Fig. 7 Photographs of texture and element mapping of sedimentary pyrite from the Huangjindong gold deposit
a. Automorphic-semi-automorphic pyrite aggregates; b. Oxygen element distribution map; c. Potassium element distribution map; d, g. Semi-automorphic-heteromorphic sedimentary pyrite aggregates, hydrothermal alteration occurred in the later stage; e. Iron element distribution map; f. Silicon element distribution map; h. Sulfur element distribution map; i. Aluminum element distribution map
5讨论5.1成矿系统中硫的来源以变质岩或沉积岩为容岩的脉状金矿床,其硫的来源一直是国际争议问题,包括沉积地层来源、同期海水来源和岩浆热液来源等观点(Burrows et al., 1986;Chang et al., 2008; Xue et al., 2013)。经典的造山型模型认为成矿物质来自赋矿围岩(如绿岩),经变质脱挥发分过程释放成矿物质进入热液成矿系统(Groves et al., 1998; Large et al., 2007)。Chang等(2008)通过收集整理矿石中热液硫化物和同期海水的硫同位素组成,发现二者具有很好的时空一致性,据此提出硫的同期海水来源模式。
黄金洞金矿床中尚未发现硫酸盐矿物,如石膏等,故硫化物S同位素的组成可近似代表成矿体系中的S同位素组成(Ohmoto, 1986)。黄金洞金矿床不同矿段热液黄铁矿δ34S值主要分布在-14.2‰~-0.5‰之间,不同于岩浆硫(δ34S=0±5‰),这导致成矿系统中S的来源存在不同认识。如董国军等(2016)用传统粉末法获得杨山庄矿段热液黄铁矿的δ34S值主要分布在-12.9‰~-5.9‰之间,认为硫不仅来源于地层,还与岩浆热液有关;夏浩东等(2017)使用传统粉末法获得华家湾矿段热液黄铁矿δ34S值主要分布在-3.7‰~-0.5‰之间,提出S具有地层和深部岩浆混合来源特征。本次研究获得围岩板岩中的沉积黄铁矿原位δ34S值为-10.7‰~-4.7‰,结合矿化石英脉周缘围岩普遍发生大规模褪色化蚀变的地质特征(许可等,2022),以及沉积黄铁矿发育的蚀变叠加结构特征(图7d、g),均暗示围岩为成矿系统贡献了S。这明显不同于湘中矿集区三叠纪脉状金矿床,如赋存在板溪群的古台山、玉横塘等金矿床。这些金矿床矿区板岩中的沉积黄铁矿的δ34S值为+15.6‰~+25.8‰,明显不同于载金热液毒砂和黄铁矿的δ34S值(多集中在0±5‰),同时这些矿床的成矿时代与周缘岩体时代一致,且矿床中普遍发育三方碲铋矿、自然铋等亲岩浆元素矿物,提出成矿作用与岩浆作用密切相关,成矿系统中的S主要来自岩浆热液(Li et al., 2019; 2021)。由此可知,江南造山带不同矿床中的S来源存在一定差异,是导致热液硫化物S同位素组成变化无明显规律的重要原因。

表1黄金洞金矿床赋矿地层中沉积黄铁矿及各矿段热液黄铁矿硫同位素数据
Table 1 Sulfur isotope data of sedimentary pyrite and hydrothermal pyrite in various ore sections of the Huangjindong gold deposit
矿段
采样位置
样品编号
测试矿物
样品数/个
δ34S/‰
资料来源
华家湾
V3矿脉
黄铁矿
5
-3.7~-0.5
夏浩东,2017
杨山庄
石英硫化物
黄铁矿
8
-10.3~-7.2
刘育,2017
金福
石英硫化物
黄铁矿
8
-10.3~-7.2
Zhang et al., 2018
金枚
黄铁矿
1
-14.2~-8.5
李荣华2020
金枚
ZK2025-4-1
沉积黄铁矿
6
-8.51
本文
ZK2025-4-2
-8.92
ZK2025-4-3
-8.98
ZK2025-5-1
-10.24
ZK2025-5-2
-10.37
ZK2025-5-3
-10.68
ZK2025-6-1
-6.52
ZK2025-6-2
-6.42
ZK2025-6-3
-6.67
ZK2025-7-1
-7.98
ZK2025-7-2
-8.21
ZK2025-7-3
-8.37
ZK2025-8-1
-4.7
ZK2025-8-2
-5.03
ZK2025-8-3
-5.11
ZK2025-9-1
-8.04
ZK2025-9-2
-8.35
ZK2025-9-3
-8.43
图8黄金洞金矿床沉积黄铁矿硫同位素分析部分打点位置图
Fig. 8 Location photograph of sulfur isotope composition of pyrite from the Huangjindong gold deposit
图9黄金洞金矿床沉积黄铁矿(Py-S)和热液黄铁矿(Py-H)硫同位素频数分布直方图(热液黄铁矿数据引自夏浩东等,2017;刘育,2017;Zhang et al., 2018;李荣华,2020)
Fig. 9 Histogram of sulfur isotope composition of sedimentary pyrite (Py-S) and hydrothermal pyrite (Py-H) from the Huangjindong gold deposit (Py-H data according to Xia et al., 2017; Liu, 2017; Zhang et al., 2018; Li et al., 2020)
5.2成矿系统中金的来源分布在变质地体中的脉状金矿床,成矿系统中Au的来源是未解决的国际难题,存在多种来源认识,如加拿大Superior和澳大利亚Yilgarn太古代克拉通地体中的脉状金矿床,赋矿镁铁质火山岩(绿岩)在增生造山过程中发生变质作用,Au等成矿物质发育活化迁移沿有利构造富集成矿(Phillips et al., 2010)。中国胶东地区“胶东型”金矿中的Au可能来自交代的岩石圈地幔(邓军等,2023)。赋存在黑色页岩和粉砂岩中的俄罗斯巨型Sukhoi Log金矿床,赋矿地层中黄铁矿的不可见w(Au)高达12×10-6,且在沉积黄铁矿周缘发育自然金,据此提出Au主要来自沉积/沉积-变质成因黄铁矿(Large et al., 2007)。
本次研究认为黄金洞赋矿围岩不是成矿系统中Au的主要来源:①马东升等(2002b)测得板溪群中的w(Au)平均为3.1×10-9,湘中地区板溪群板岩中的黄铁矿w(Au)(< 1.6×10-6)(Li et al., 2018),表明地层中的Au并没有发生明显的富集;②沉积黄铁矿中的不可见w(Au)低于1.0×10-6(表2),且在沉积黄铁矿周缘也未见自然金分布,因此推测沉积黄铁矿中的不可见金发生活化迁移提供大量金的可能性不大;③沥青等有机物能够运移和富集金(Taylor et al.,1989),而围岩中没有沥青等有机质的报道,因此排除其富集Au的可能。
5.3矿床成因成矿物质、成矿流体和成矿时代的精确厘定,是揭示矿床成因的关键。如前所述,黄金洞矿床含金石英脉中普遍发育白钨矿,且白钨矿呈角砾被晚期热液硫化物胶结(图4),暗示钨成矿作用时限应为金成矿作用的上限。周岳强等(2021)获得黄金洞矿床中白钨矿Sm-Nd等时线年龄为(129.7±7.4)Ma,表明金成矿作用发生于燕山期古太平洋板块向华南板块俯冲后撤的拉伸背景下(Xu et al., 2017),暗示黄金洞矿床的形成明显不同于造山型金矿床,后者主要形成于增生造山或俯冲造山挤压背景。黄金洞石英的δ18OH2O值介于5.1‰~9.9‰,δD值介于-56‰ ~-64‰,主要分布在岩浆水范围(毛景文等,1997)。综合上述分析,本文认为深部隐伏岩浆作用为黄金洞矿床的形成提供了成矿物质(Xu et al., 2017; Deng et al., 2020)。成矿流体在与围岩相互作用过程中,沉积成因的硫加入成矿系统,导致热液毒砂和黄铁矿的δ34S值明显具有混合来源特征,水岩反应是驱使沉积成因S加入成系统的重要机制。
图10黄金洞金矿床沉积黄铁矿LA-ICP-MS不同测试元素信号随时间变化图解
Fig. 10 Time variation diagram of LA-ICP-MS test of different elements from sedimentary pyrite of the Huangjindong deposit
6结论(1)黄金洞金矿床赋矿围岩普遍发育沉积黄铁矿,水岩相互作用过程诱发沉积成因硫加入成矿系统,导致热液硫化物硫同位素组成明显不同于典型岩浆热液矿床。
(2)黄金洞金矿床赋矿围岩沉积黄铁矿中的不可见w(Au)多低于1×10-6,不是成矿系统中金的主要来源,结合成矿年代学等证据,认为成矿物质主要来自深部岩浆热液。

表2黄金洞金矿床沉积黄铁矿LA-ICP-MS微量元素组成(w(B)/10-6)
Table 2 LA-ICP-MS trace element (w(B)/10-6) composition of sedimentary pyrite deposited of the Huangjindong gold deposit
样品编号
Au
As
Sb
W
Co
Ni
Cu
V
Cr
Pb
Bi
Se
Te
ZK2025-4@1
0.1
2566
20.4
5.3
99.3
116.5
4.9
6.4
34.0
265.5
8.6
9.4
6.2
ZK2025-4@2
0.1
2535
15.8
10.8
125.7
179.9
4.5
20.5
47.6
37.2
5.3
16.7
3.6
ZK2025-4@3
-
1678
13.8
15.2
80.3
89.1
5.2
10.8
52.2
28.6
3.8
5.6
2.2
ZK2025-4@4
-
3414
13.0
0.3
328.4
662.7
5.8
43.6
93.7
165.0
10.2
10.7
30.2
ZK2025-4@5
0.8
10666
6.2
1.2
1.7
4.3
-
3.7
8.8
140.9
2.1
30.2
9.4
ZK2025-6@1
0.1
2022
20.2
0.4
62.2
177.1
4.3
9.5
17.1
37.5
1.5
5.7
0.9
ZK2025-6@2
0.2
1567
63.8
1.2
35.7
163.9
25.9
48.5
45.4
181.2
2.2
5.7
2.3
ZK2025-6@3
0.1
1345
34.9
1.8
54.5
147.8
8.9
24.0
36.9
74.7
1.7
4.7
1.1
ZK2025-6@4
0.2
4279
11.6
0.5
96.1
338.8
1.8
1.5
-
23.8
0.8
14.1
11.4
ZK2025-6@5
0.2
2078
13.7
6.9
66.7
253.4
4.1
2.4
5.2
35.2
0.6
4.9
1.4
ZK2025-9@1
0.1
3974
7.7
1.0
33.5
41.4
3.9
12.7
13.7
54.9
2.3
7.6
2.1
ZK2025-9@2
0.2
4871
13.6
0.6
27.7
43.6
4.1
3.2
6.9
851.7
5.2
10.1
4.8
ZK2025-9@3
0.4
8903
2.5
0.5
20.3
75.9
-
-
-
10.4
0.7
20.4
11.1
ZK2025-8@1
0.8
8446
15.0
8.5
4.9
20.2
9.7
33.3
56.2
1667.0
7.3
19.0
22.7
ZK2025-8@2
-
1628
3.0
0.9
6.7
5.7
-
2.9
7.8
6.6
0.9
5.5
-
ZK2025-8@3
-
795
-
-
0.8
-
-
-
-
272.5
1.9
4.1
-
ZK2025-8@4
-
1586
1.7
0.4
15.4
13.3
2.7
-
-
6.7
0.5
3.8
1.1
ZK2025-8@5
0.3
5651
6.4
-
8.7
38.1
3.7
1.6
9.6
19.2
1.3
14.8
8.5
ZK2025-5@1
0.1
1339
-
-
0.7
44.0
-
-
-
7.3
0.2
4.2
-
ZK2025-5@2
-
1022
-
0.4
2.2
3.4
-
-
-
0.7
0.1
-
-
ZK2025-5@3
-
799
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
3.3
-
ZK2025-5@4
-
4090
1.8
5.6
9.7
79.6
-
3.6
6.9
9.5
0.9
29.8
6.7
ZK2025-5@5
-
1778
-
-
1.5
7.6
-
-
-
0.2
0.0
8.3
-
ZK2025-7@1
0.3
6608
-
0.8
5.6
14.4
-
-
-
1.2
0.1
18.9
5.1
ZK2025-7@2
0.8
5757
2.0
4.0
39.2
5.7
-
0.6
-
6.5
0.5
18.5
5.2
ZK2025-7@3
0.7
6251
5.8
0.6
78.7
84.4
2.4
0.5
-
26.3
1.4
20.4
2.6
ZK2025-7@4
0.9
6140
1.5
-
-
-
-
-
-
3.9
0.3
17.0
3.5
ZK2025-7@5
1.0
7526
3.9
7.2
51.4
17.6
4.8
-
-
12.6
1.1
13.1
1.9
注:“-”为低于检测限。
图11黄金洞金矿床沉积黄铁矿(Py-S)和热液黄铁矿(Py-H)微量元素组成对比(热液黄铁矿微量元素数据据吴俊等, 2023)
Fig. 11 Comparison of trace elements of sedimentary pyrite (Py-S) and hydrothermal pyrite (Py-H) of the Huangjindong deposit (data of trace elements of hydrothermal pyrite are from Wu et al., 2023)
致谢野外工作期间得到了湖南省地质灾害调查监测所董国军教授级高工,吴俊、周岳强、范鹏、王翔等工程师的大力支持与帮助。河北工程大学李长平老师给予野外和室内测试分析指导。测试分析过程中得到了中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所陈振宇老师、侯可军老师和王倩老师的悉心指导,在此一并致谢。
-
参考文献
摘要
黄金洞大型金矿床位于江南造山带湘东北矿集区,矿体主要赋存于沉积黄铁矿发育的新元古代冷家溪群板岩中,含金石英脉为主要的矿化类型。为进一步约束成矿系统中金和硫的来源,揭示赋矿围岩对成矿贡献,深化矿床成因认识,文章以赋矿围岩冷家溪群板岩为研究对象,对其沉积黄铁矿进行了系统的岩相学、电子探针显微结构、激光剥蚀等离子质谱(LA-ICP-MS)原位微量元素和硫同位素分析。研究结果显示,冷家溪群板岩中的沉积黄铁矿主要呈团块状集合体,单个颗粒多为几百~几千微米。微量元素分析结果表明,沉积黄铁矿w(As)变化范围介于796×10-6~10 667×10-6,不可见w(Au)多低于1.0×10-6。沉积黄铁矿的原位δ34S值主要介于-10.7‰~-4.7‰,与矿石中的热液黄铁矿(δ34S=-14.2‰~-0.5‰)具有一定相似性。以上分析结果暗示,沉积黄铁矿提供成矿系统中的金的可能性不大,推测黄金洞金矿床Au主要来自深部过程。成矿流体在与围岩相互作用过程中,沉积成因硫加入成矿系统,为解释热液成因黄铁矿硫同位素组成特征提供关键证据。
Abstract
The Huangjindong gold large-scale deposit is located in the northeastern Hunan ore cluster, Jiangnan orogenic belt, and the ore bodies mainly occur in the slate of the Neoproterozoic Lengjiaxi Group, and auriferous quartz vein is the main ore type. In order to further restrict the sources of gold and sulfur in the ore-forming system, reveal the role of wallrock to the mineralizing system, and finally make a better understanding of the genesis This paper focuses on the sedimentary pyrite from slate of the Lengjiaxi Group, systematic analyses including petrography, microstructure using electron probe, laser in situ trace elements and sulfur isotope were conducted. The results show that sedimentary pyrite occurs as assemblages and the individuals is mostly of hundreds to thousands ofμm in size. LA-ICP-MS trace element analytical results show thatw(As) concentrations vary from 796×10-6to 10 667×10-6,and invisiblew(Au) is mostly less than 1.0×10-6. In situ S isotope analytical results reveal thatδ34S value of sedimentary pyrite mainly ranges from-10.7‰ to-4.7‰, which is similar to the hydrothermal pyrite in the ore (δ34S =-14.2‰ to-0.5‰). All results suggest that the majority of Au is sourced from wallrock, indicating Au is mainly associated with deep processes. During the fluid-rock interaction processes, sedimentary sulfur added to the mineralization system, which gives implications for the interpretation of S isotope composition of hydrothermal pyrite in Huangjindong deposit.