-
以锂为代表的稀有金属是关系中国战略性新兴产业发展的关键矿产资源,加强其找矿勘查工作,提高资源保障程度,关系到国家的能源资源安全(王登红等,2019)。华南是中国稀有金属的重要产地(李建康等,2014;2023;王成辉等,2022),其中,赣西北地区锂铍铌钽稀有金属成矿地质条件优越。近年来随着云母型锂矿的大规模开发利用,使得赣西北地区乃至华南地区产于花岗岩中的云母型锂矿备受瞩目(王成辉等,2022)。赣西北地区稀有金属矿化集中于武功山、九岭两个成矿带,代表性矿床有著名的宜春414铌钽锂矿和白水洞锂铌钽矿(黄小龙等,2001;Xie et al.,2019)。近年来的研究和勘查工作表明,九岭地区狮子岭稀有金属矿化花岗岩岩相分带与武功山地区宜春414铌钽矿具有一定的相似性,但矿物组成上有较高含量的磷锂铝石、绿柱石和铌钽矿物(王成辉等,2018),稀有金属成矿潜力巨大(秦程,2018;孙艳等,2018;王成辉等,2019)。特别是以磷锂铝石为造岩矿物的花岗岩在国内首次发现,这为在九岭地区寻找稀有金属矿床提供了重要的新方向(杨岳清等,2021)。
狮子岭岩体为九岭地区新发现的花岗岩型锂等稀有金属矿化岩体,其Li2O平均品位0.75%,预测资源量达5.9万t,通过重力场—强磁场—电场物理选矿后再经二次富集,Li2O的原矿(1.08%)可成为5.17%的精矿(王成辉等,2019)。前人对狮子岭岩体的矿物学特征、稀有金属成矿潜力及矿化特征已有初步探讨(秦程,2018;王成辉等,2018;2019;刘泽等,2023),但对其成岩成矿时代及稀有金属成矿机制研究不足。因此,深入研究狮子岭岩体岩相学、年代学和岩石地球化学特征等对赣西北稀有金属成矿作用和找矿方向具有重要意义。
本文通过对狮子岭地区矿化花岗岩进行锆石U-Pb年代学及全岩主微量元素分析工作,限定狮子岭成岩时代及稀有金属成矿时代,进而讨论狮子岭岩体地球化学特征及稀有金属成矿过程,为赣西北稀有金属成矿理论和找矿勘查工作提供进一步的理论支撑。
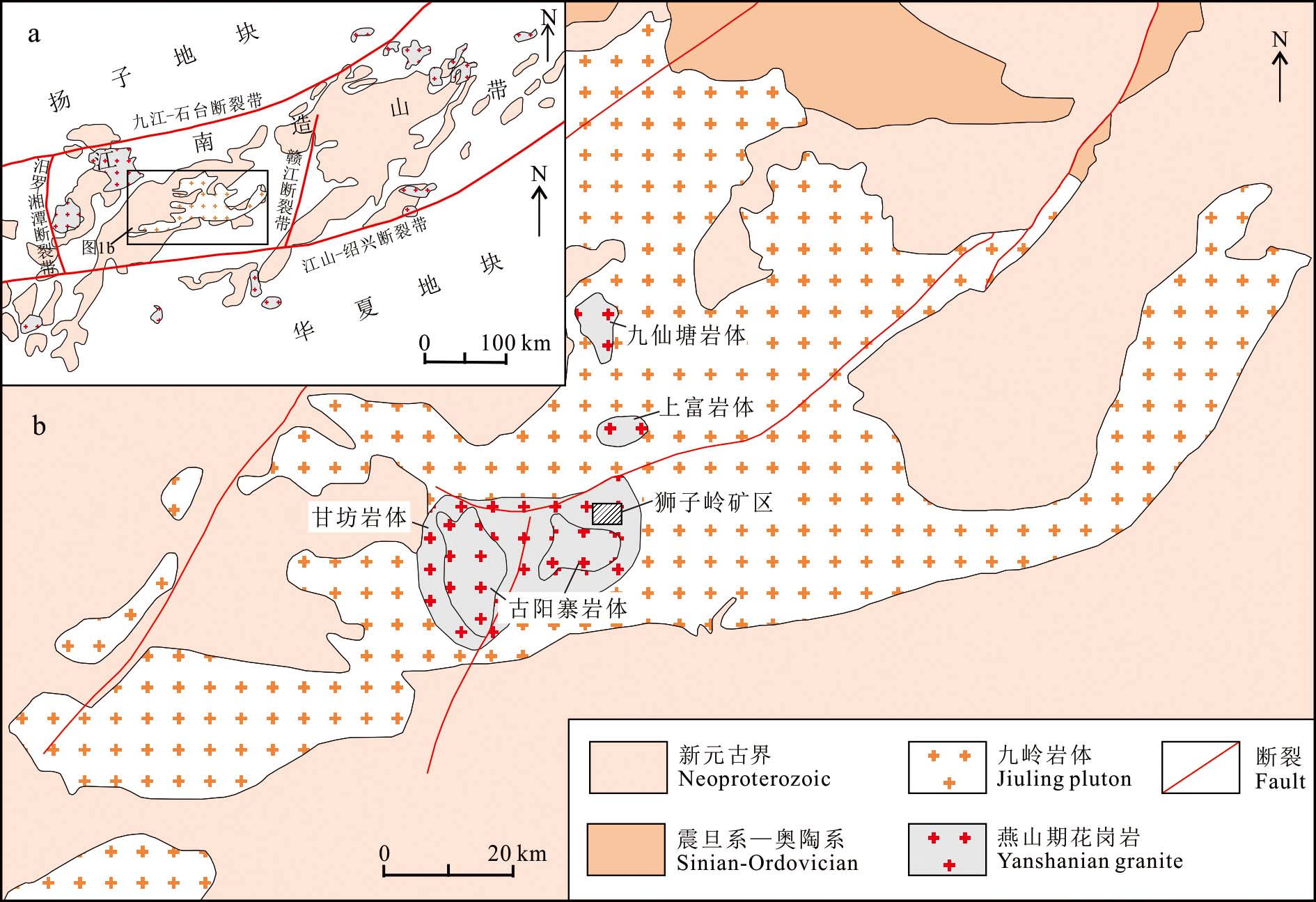
1地质背景1.1区域地质背景九岭地区地处华夏地块及扬子地块之间中新元古代洋盆闭合所形成的江南造山带中段(Wang et al.,2014),东界为近南北向的赣江断裂带,西界为近南北向汨罗-湘潭断裂带,南界为近东西向的江山-绍兴断裂带,北界临近东西向九江-石台断裂带(图1a)。区内北东向断裂是主要控矿构造,控制着岩浆活动、地层及稀有金属矿脉的产出。出露地层为新元古界双桥山群,厚度达4 km,岩性为二云母片岩、变余凝灰质砂岩、泥质砂屑千枚岩,夹有细碧岩-石英角斑岩(王成辉等,2019)。在九岭地区内,发生较为广泛的中酸性岩浆侵入活动,侵入时代从新元古代一直到新生代。最老侵入岩为新元古代九岭岩体,岩体近东西向—北东东向展布,侵入于双桥山群变质沉积岩中,出露面积可达2500 km2,为华南地区出露面积最大的新元古代花岗质侵入体(Li et al.,2003)。对于九岭岩体已有诸多学者进行过年代学研究,年龄结果主要集中于836~808 Ma(Li et al.,2003;Zhao et al.,2013;孙克克等,2017;段政等,2019;张福神等,2020;张志辉等,2021)。
图1江南造山带中段地质简图(a,据Wang et al.,2014修改)、九岭地区地质简图(b,据钟玉芳等,2005修改)
Fig.1 Simplified geological map of the middle section of the Jiangnan orogenic belt (a, modified after Wang et al., 2014), simplified geological map of the Jiuling area (b, modified after Zhong et al., 2005)
九岭岩体是由中生代花岗质岩浆多次侵入形成的,广泛分布有燕山期上富、甘坊及古阳寨等岩体,这些岩体多为复式岩体。甘坊岩体的规模最大,侵位于九岭岩体中部,出露面积达400 km2,近东西向延伸(图1b)。其主体岩性由老至新为黑云母花岗岩→二云母花岗岩→钠长石化白(锂)云母花岗岩(周建廷等,2011)。相比于九岭岩体,甘坊岩体的花岗岩颜色较浅,白云母偏多,矿物颗粒也比较粗大,岩石化学成分趋于高硅、富碱(秦程,2018)。甘坊岩体为多期次多阶段岩浆侵入形成的复式岩体,其侵入活动高峰发生于晚侏罗世及早白垩世(Wang et al.,2017; 2022;Xie et al.,2019;聂晓亮等,2022;Ouyang et al.,2023),本文研究的狮子岭岩体在早白垩世侵位于甘坊岩体中。
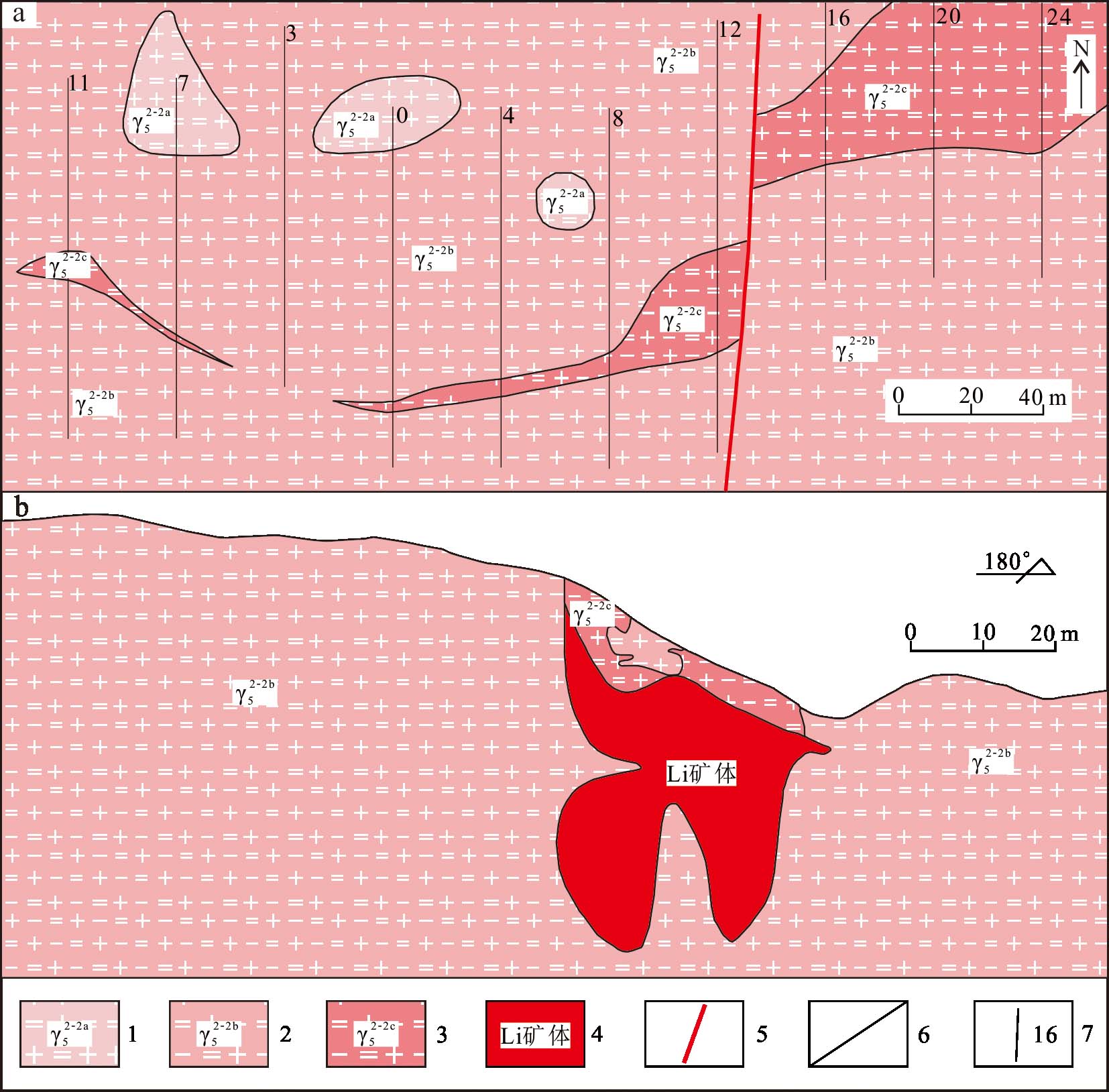
1.2狮子岭矿区地质特征狮子岭岩体侵位于甘坊岩体东北部(图2)。狮子岭岩体由早到晚可划分为黑云母二长花岗岩、二云母碱长花岗岩、锂(白)云母碱长花岗岩和黄玉-锂云母碱长花岗岩,具有雅山岩体相似的分带特征(李洁等,2013;杨泽黎等,2014;王成辉等,2019)。从黑云母二长花岗岩到发生Li、Nb、Ta矿化的二云母碱长花岗岩、锂(白)云母碱长花岗岩和黄玉-锂云母碱长花岗岩为同源岩浆经不同期次侵入后分异结晶形成。狮子岭岩体中矿化花岗岩由早到晚,稀有金属矿化强度逐渐增加,出露面积达0.7 km2,呈岩株状侵入到黑云母二长花岗岩中(图3a)。狮子岭矿化花岗岩矿物组合具有明显演化规律,如二云母碱长花岗岩→锂(白)云母碱长花岗岩→黄玉-锂云母碱长花岗岩的岩石结构由等粒花岗结构向斑状结构演化;钾钠长石含量由钾长石多向钠长石多转变;稀有金属矿物含量由少到多,种类逐渐复杂;云母类型向着锂云母端员演化(王成辉等,2019)。目前研究表明矿化岩体中云母族矿物存在两个演化序列,白云母→锂白云母→锂云母演化序列和铁叶云母→黑鳞云母→铁锂云母→锂云母演化序列(刘泽等,2023)。此外,王成辉等(2018)在狮子岭岩体首次发现了磷锂铝石,这也是在九岭成矿带首次发现该矿物。磷锂铝石在锂(白)云母碱长花岗岩中约占2%~3%,在黄玉-锂云母碱长花岗岩中高达4%~7%,可列为造岩矿物(孙艳等,2018)。
图2狮子岭矿区地质简图(a)及16号勘探线剖面图(b)(据周建廷等,2013修改)1—燕山早期第二阶段第一次侵入二云母花岗岩;2—燕山早期第二阶段第二次侵入白云母花岗岩;3—燕山早期第二阶段第三次侵入白云母花岗岩;4—锂矿体;5—断裂;6—地质界线;7—勘探线及编号
Fig.2 Simplified geological map of the Shiziling deposit (a) and cross section at prospecting line 16 through the deposit (b) (modified after Zhou et al., 2013)1—The first phase intrusion of two-mica granite in the second stage of Early Yanshanian; 2—The second phase intrusion of muscovite granite in the second stage of Early Yanshanian; 3—The third phase intrusion of muscovite granite in the second stage of Early Yanshanian; 4—Li ore body;5—Fault; 6—Geological boundary; 7—Prospecting line and its number
2样品采集及分析方法2.1样品采集及岩相学观察笔者在狮子岭地区(114°56′53″E、28°36′46″N)地表露头采集了黑云母二长花岗岩、二云母碱长花岗岩、锂(白)云母碱长花岗岩及黄玉-锂云母碱长花岗岩样品共8件(表1),对全部样品进行全岩主量、微量元素分析,同时选择黑云母二长花岗岩及二云母碱长花岗岩样品(YFSZL-1、YFSZL-3)进行了LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年测定。
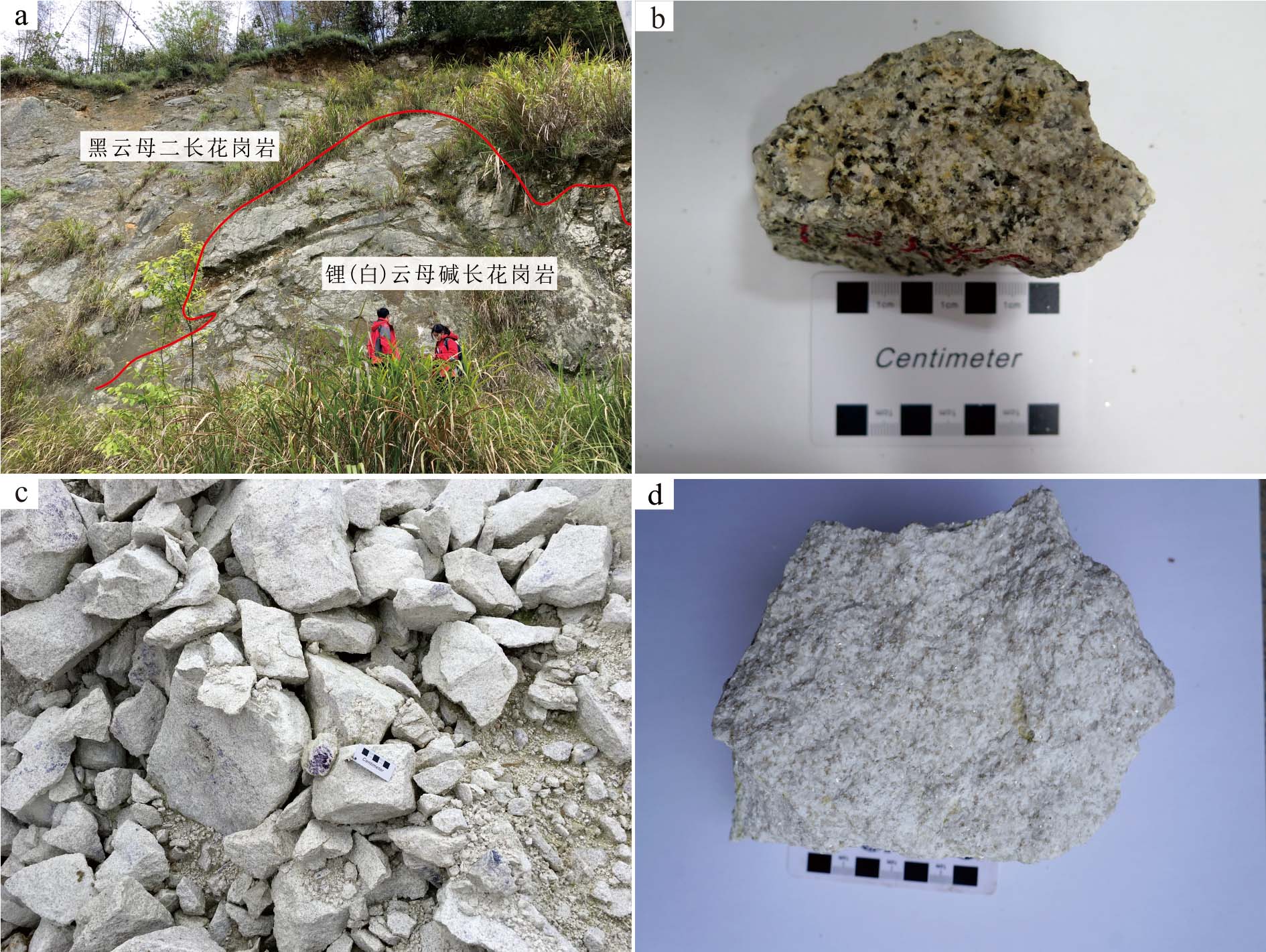
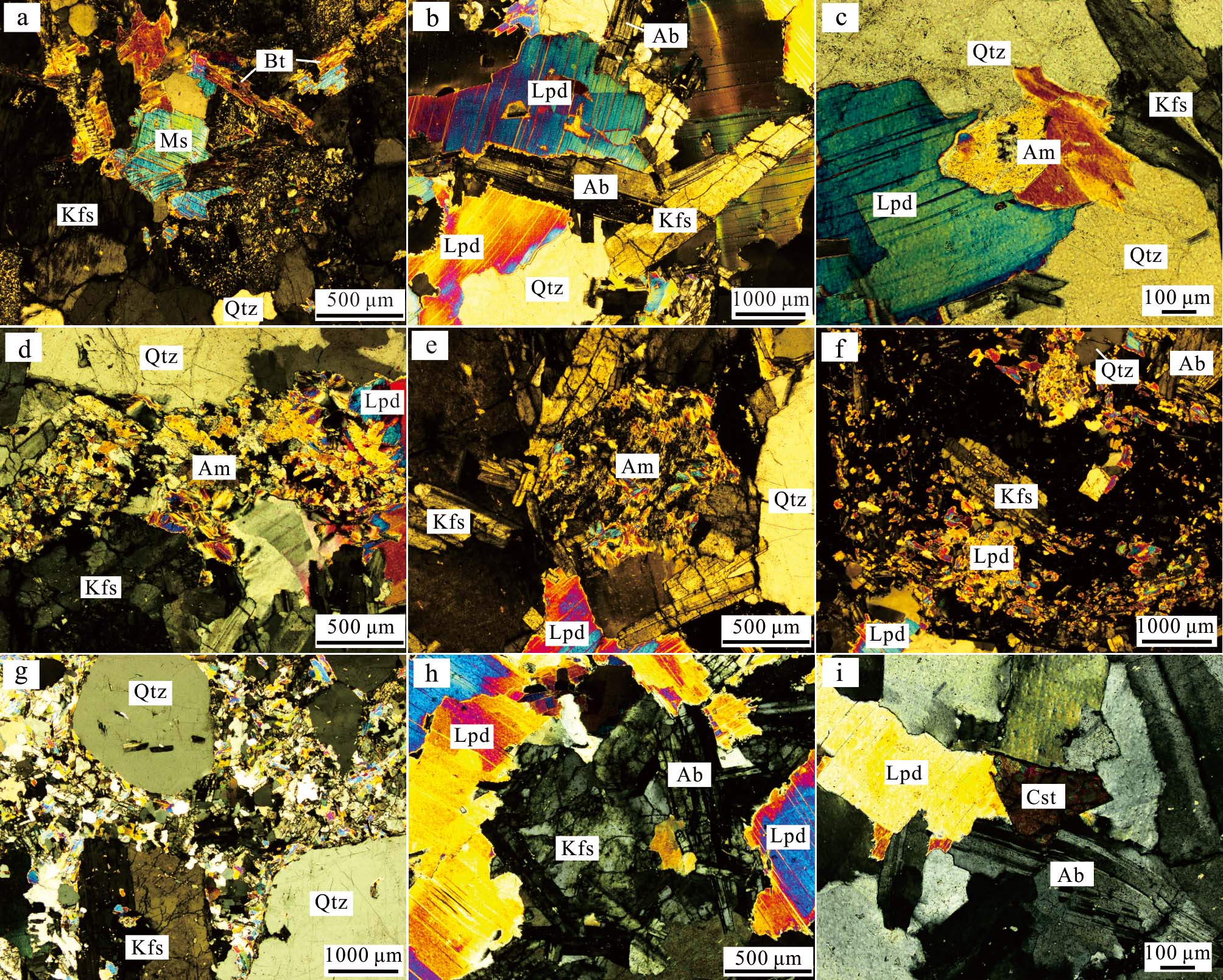
图3狮子岭花岗岩野外及手标本照片 a. 锂(白)云母碱长花岗岩与黑云母二长花岗岩侵入接触关系;b. 黑云母二长花岗岩;c、d. 锂(白)云母碱长花岗岩
Fig.3 Field occurrences and hand specimens of Shiziling granites a. Contact relationship of lepidolite (muscovite) alkali feldspar granite and biotite monzogranite;b. Biotite monzogranite;c, d. Lepidolite (muscovite) alkali feldspar granite
表1狮子岭花岗岩样品名称及造岩矿物组成
Table 1 Name of the sample and rock forming mineral composition of Shiziling granites
样品编号
岩性
造岩矿物组成
SZL-1
黑云母二长花岗岩
石英(35%)+钾长石(30%)+斜长石(27%)+黑云母(5%)
SZL-2
二云母碱长花岗岩
石英(35%)+钾长石(40%)+钠长石(10%)+白云母、黑鳞云母(10%)
SZL-3
锂(白)云母碱长花岗岩
石英(40%)+钾长石(20%)+钠长石(20%)+锂(白)云母、磷锂铝石(18%)
SZL-4
锂(白)云母碱长花岗岩
石英(45%)+钾长石(20%)+钠长石(20%)+锂(白)云母、磷锂铝石(9%)
SZL-5
锂(白)云母碱长花岗岩
石英(43%)+钾长石(18%)+钠长石(25%)+锂(白)云母、磷锂铝石(10%)
SZL-6
锂(白)云母碱长花岗岩
石英(40%)+钾长石(20%)+钠长石(25%)+锂(白)云母、磷锂铝石(13%)
SZL-7
黄玉-锂云母碱长花岗岩
石英(25%)+钾长石(20%)+钠长石(25%)+锂云母、磷锂铝石(15%)+黄玉(8%)
SZL-8
黄玉-锂云母碱长花岗岩
石英(30%)+钾长石(20%)+钠长石(25%)+锂云母、磷锂铝石(17%)+黄玉(6%)
2.2实验方法全岩主、微量元素分析在国家地质实验测试中心完成。分析仪器为Thermo ElementⅡ等离子质谱仪,激光剥蚀系统为New Wave UP-213。实验采用He作为剥蚀物质的载气,激光波长213 nm、束斑40 μm、脉冲频率10 Hz、能量0.176 mJ、密度23~25 J/m2,测试过程中首先遮挡激光束进行空白背景采集15 s,然后进行样品连续剥蚀采集45 s,停止剥蚀后继续吹扫15 s清洗进样系统,单点测试分析时间75 s。等离子质谱测试参数为冷却气流速(Ar)15.55 L/min,辅助气流速(Ar)0.67 L/min,载气流速(He)0.58 L/min;样品气流速0.819 L/min,射频发生器功率1205 W。测试采用标样为美国地调局标准样品(USGS-Standard MASS-1)。硫化物微量元素测试精度优于10%,检出限为10-9。
锆石LA-ICP-MS测试在自然资源部成矿作用与资源评价重点实验室完成。本次挑选SZL-1、SZL-3新鲜样品各5 kg。锆石挑选过程中先把样品破碎,后将碎样放入直径为20 cm的不锈钢钵中,在XZW100型振动磨样机中研磨3~5 s后取出,此过程反复进行直至样品全部通过0.3 mm孔径筛,然后洗去粉尘,经铝制淘砂盘富集重矿物,再通过磁选、电磁选分离出非电磁部分,而后淘洗获得锆石精矿,最后在双目镜下挑选出用于定年的锆石颗粒。将待测锆石样品、91500锆石标准和人工合成的NIST612硅酸盐玻璃分别用胶粘在载玻片上,放上PVC环,然后将环氧树脂和固化剂进行充分混合后注入PVC环中,待树脂充分固化后将样品座从载玻片上剥离,并对其进行抛光(侯可军等,2009)。用酒精轻擦样品表面后,利用Finnigan Neptune型多接收电感耦合等离子体质谱仪及与之配套的Newwave UP-213激光剥蚀系统建立的锆石微区U-Pb定年技术对锆石进行详细的年代学研究。激光剥蚀系统参数同上。等离子体质仪参数为冷却气流速(Ar)15 L/min,辅助气流速(Ar)0.6 L/min,射频发生器功率1200 W,空白采集时间27 s。年龄权重计算及谐和图绘制均采用Isoplot 3.0(Ludwig,2003)完成。
图4狮子岭花岗岩镜下照片a. 二云母碱长花岗岩中黑鳞云母交代穿切白云母;b. 锂(白)云母碱长花岗岩中钠长石穿切锂云母;c. 锂(白)云母碱长花岗岩中锂云母与磷锂铝石伴生;d. 锂(白)云母碱长花岗岩中经交代作用破碎的磷锂铝石;e. 锂(白)云母碱长花岗岩中磷锂铝石发生锂云母化;f. 锂白云母碱长花岗岩中不同成因的锂云母;g. 黄玉-锂云母碱长花岗岩中石英和钾长石构成斑晶;h. 黄玉-锂云母碱长花岗岩中钾长石交代穿切锂云母;i. 黄玉-锂云母碱长花岗岩中锂云母、钠长石间夹有含钽锡石Lpd—锂云母;Qtz—石英;Ab—钠长石;Kfs—钾长石;Ms—白云母;Bt—黑鳞云母;Am—磷锂铝石;Cst—锡石
Fig.4Photomicrographs of specimen from the Shiziling granites a. Muscovite is replaced by protolithionite in two-mica alkali feldspar granite; b. Albite cut lepidolite in lepidolite (muscovite) alkali feldspar granite;c. Lepidolite associates with amblygonite in lepidolite (muscovite) alkali feldspar granite; d. Amblygonite broken by metasomatism in lepidolite (muscovite) alkali feldspar granite; e. Amblygonite is alterded to lepidolite in lepidolite (muscovite) alkali feldspar granite; f. Different genesis of lepidolite in lepidolite (muscovite) alkali feldspar granite; g. Quartz and K-feldspar form phenocrystal in topaz-lepidolite alkali feldspar granite; h. K-feldspar cut lepidolite in topaz-lepidolite alkali feldspar granite; i. Cassiterite is located at the junction of lepidolite and albite in topaz-lepidolite alkali feldspar granite Lpd—Lepidolite; Qtz—Quartz; Ab—Albite; Kfs—K-feldspar; Ms—Muscovite; Bt—Protolithionite; Am—Amblygonite; Cst—Cassiterite
3岩相学特征及分析结果3.1岩相学特征黑云母二长花岗岩,细粒花岗结构,块状构造(图3b)。主要矿物为石英、钾长石、斜长石和黑云母。石英呈他形粒状,钾长石和斜长石均以半自形板状为主,镜下观察黑云母粒径约0.8~1.4 mm,呈不规则片状零散分布,正中突起,部分黑云母穿插斜长石,可见少量自形片状白云母,具一组极完全解理,含量约1%。斜长石难见聚片双晶,受蚀变影响,矿物颗粒表面裂纹发育。可见少量磁铁矿、磷灰石和锆石等副矿物。
二云母碱长花岗岩,细粒花岗结构,块状构造。主要矿物为石英、钾长石、钠长石、白云母和黑鳞云母。石英呈他形粒状分布于长石颗粒之间,钾长石呈半自形板状,可分为2期,晚期钾长石粒度略大,平均0.8 mm,部分可达1.2 mm,且数量比早期钾长石多。钠长石呈半自形板柱状,粒度普遍小于钾长石,平均0.5 mm,可见部分钠长石发生绢云母化。云母种类初步认为是白云母和黑鳞云母。白云母呈自形片状,粒径约0.2~0.5 mm,一组极完全解理,干涉色可达三级蓝绿,形成时间早于黑鳞云母,部分白云母被后期黑鳞云母交代穿切(图4a)。可见黑鳞云母与铌钽矿物伴生,且在部分黑鳞云母中可见锆石和磷灰石等副矿物。
锂(白)云母碱长花岗岩,细-中粒花岗结构,块状构造(图3d)。主要矿物为石英、钾长石、钠长石、锂(白)云母和磷锂铝石。石英呈他形粒状,相比于二云母碱长花岗岩,粒度更大,含量更高,也有较晚期形成的细粒石英。钾长石呈半自形板状,粒度变化较大,粒径约0.6~1.5 mm,最大可达2.5 mm,部分略有泥化。钠长石呈自形板状,粒径约0.3~1.2 mm,部分钠长石穿切锂云母(图4b)。磷锂铝石粒径约0.2~0.5 mm,呈半自形板柱状,有时可见极细密的聚片双晶,正低至正中突起,干涉色均在一级顶部,可见其生长于钾长石、石英和锂云母的颗粒之间(图4c),边部多发生蚀变(图4d、e)。除自形程度较好的岩浆结晶成因锂云母外,可见后期交代蚀变形成的小颗粒锂云母生长于长石边部或内部(图4f)。此外,可见黄玉、锆石、萤石等副矿物。
黄玉-锂云母碱长花岗岩,具有似斑状结构,块状构造。主要矿物为石英、钾长石、钠长石、锂云母和黄玉。斑晶为石英和钾长石,粒度是其他矿物的5~10倍,形成较早。似斑状结构表现为2种形式:一种是以钾长石为主,少部分钠长石自形晶分布其中;另一种是形成较晚的细粒钾长石、钠长石、石英和云母-黄玉集合体,交代或叠加在早期矿物之上,且有磷锂铝石、铌钽矿等矿物(图4g)。在样品中多见长石、云母等矿物形成的花岗结构,未见宜春414矿石中普遍发育的雪球结构。钾长石呈半自形板柱状产出,粒度相差较大,可分为2期。早期钾长石粒径约0.5~1.0 mm,晚期钾长石粒度较小,且数量少。钠长石以自形板柱状为主,部分为半自形,也可分为2期,早期钠长石为典型的自形板柱状,粒径约0.5~1.2 mm,晚期钠长石呈半自形短柱状,且含量少。锂云母多为半自形片状-板状,最高干涉色达二级紫红,早于长石形成,镜下可见半自形板柱状钾长石交代锂云母及自形钠长石穿切锂云母(图4h)。黄玉多为半自形-他形粒状产出,形成较早,多被钠长石交代。磷锂铝石呈他形粒状嵌布于钾长石和石英颗粒之间,部分磷锂铝石被云母强烈交代而发生破碎。另外可见铌钽矿物、含钽锡石(图4i)。
3.2全岩主量、微量元素8件样品全岩主微量元素分析结果见表2。矿化岩体的主量元素具有以下地球化学特征:①SiO2含量较高,w(SiO2)介于70.08%~73.06%之间,TAS图解中样品均投点在典型花岗岩范围内(图5a);②富铝,w(Al2O3)介于15.89%~17.79%之间,铝指数(A/NK)达1.53~2.1,铝饱和指数(A/CNK)为1.42~1.95,在A/NK-A/CNK图解(图5b)中样品均投点在强过铝质区域内;③碱含量中等,w(Na2O)为1.1%~4.2%,w(K2O)为3.57%~5.47%,全碱w(Na2O+K2O)变化在6.57%~7.81%,由K2O-SiO2图解(图5c)和SiO2-AR图解(图5d)中可知,样品为高钾钙碱性系列;④贫钙、钛、铁、镁,w(CaO)最高不超过0.77%,CaO/Na2O值极低,介于0.02~0.28之间,w(TiO2)、w(Fe2O3)、w(FeO)、w(MgO)分别为0.01%~0.26%、0.03%~0.76%、0.77%~1.32%和0.05%~0.33%。分异指数(DI)介于89.54~92.26,表明岩体经过较高程度岩浆分异演化;⑤磷含量较高,w(P2O5)均在0.2%以上,特别是锂(白)云母碱长花岗岩,w(P2O5)最高可达0.74%,与I型和A型花岗岩质熔体w(P2O5)较低(约0.1%,Harrison et al.,1984)的特点有明显区别。结合岩石中常见黄玉、萤石等富氟矿物,可归类为富氟高磷花岗岩,这一特征与雅山岩体相近(黄小龙等,2001;Yin et al.,2022)。黑云母二长花岗岩同样高硅(w(SiO2)=72.64%)、富铝(w(Al2O3)=15.13%),但相比于矿化花岗岩具有相对高的全碱含量(w(Na2O+K2O)= 8.26%),相对低的铝指数(A/NK=1.42)、铝饱和指数(A/CNK=1.32)和磷含量(w(P2O5)=0.15%)。
表2狮子岭花岗岩全岩主量(w(B)/%)、微量及稀土元素(w(B)/10-6)分析结果
Table 2 Whole-rock major(w(B)/%), trace and rare earth elements(w(B)/10-6)analytical results of rock samples from the Shiziling granites
组分
黑云母二长花岗岩
二云母碱长花岗岩
锂(白)云母碱长花岗岩
黄玉-锂云母碱长花岗岩
SZL-1
SZL-2
SZL-3
SZL-4
SZL-5
SZL-6
SZL-7
SZL-8
SiO2
72.64
70.36
70.08
72.24
72.3
70.59
73.06
72.39
TiO2
0.23
0.26
0.01
0.01
0.11
0.01
<0.01
<0.01
Al2O3
15.13
16.2
17.77
16.39
15.89
17.79
16.59
16.29
Fe2O3
0.32
0.76
<0.05
0.04
0.03
<0.05
<0.05
<0.05
FeO
1.44
1.31
0.85
0.79
1.32
0.82
0.77
0.87
MnO
0.07
0.05
0.15
0.16
0.09
0.15
0.15
0.14
MgO
0.39
0.33
<0.05
<0.05
0.19
<0.05
<0.05
<0.05
CaO
0.41
0.31
0.77
0.09
0.06
0.13
0.2
0.6
Na2O
3.1
1.1
3.88
3.11
2.45
3.66
4.2
3.95
K2O
5.16
5.47
3.71
3.79
4.51
3.83
3.61
3.57
P2O5
0.15
0.36
0.74
0.47
0.46
0.58
0.2
0.46
CO2
0.37
0.31
0.28
0.46
0.28
0.35
0.35
0.72
H2O+
1.05
2.93
2.19
1.96
2.16
2.26
1.38
1.1
LOI
1.18
3.03
2.41
2.49
2.32
2.63
1.66
1.78
总和*
100.22
99.54
100.42
99.61
99.73
100.24
100.50
100.11
A/NK
1.42
2.10
1.71
1.78
1.78
1.75
1.53
1.57
A/CNK
1.32
1.95
1.51
1.75
1.76
1.71
1.48
1.42
AKI
0.71
0.48
0.59
0.56
0.56
0.57
0.65
0.64
DI
90.64
90.50
90.01
91.15
89.54
90.30
91.90
92.26
Li
297
691
2009
1849
1052
2747
3325
3260
Be
21.4
37.8
182
174
37.5
144
171
221
Cr
20.9
26.3
14.5
8.59
18.6
14.3
15.3
20.7
Mn
533
396
1177
1095
578
1055
1204
1208
Co
2.9
2.12
1.26
0.57
1.3
1.56
0.62
0.51
Ni
3.5
3.83
1.97
1.16
2.01
1.85
1.53
1.25
Cu
60.7
109
11.5
13.7
11
3.06
4.51
4.94
Zn
66.1
72.1
130
103
61.4
125
142
152
Ga
23.9
26
32.5
27.6
26.4
27.3
28.5
28.8
Rb
415
630
1736
1779
969
2067
2251
2291
Sr
55.1
39.9
19.6
18.7
20
16.8
3.65
11.6
Mo
0.46
0.18
0.17
0.26
0.17
0.28
0.32
0.21
Cd
<0.05
<0.05
0.08
<0.05
0.07
0.15
0.15
0.12
In
0.06
0.06
<0.05
<0.05
0.06
<0.05
<0.05
<0.05
Cs
86.1
235
314
450
246
525
509
515
Ba
255
287
8.03
6.44
107
7.12
2.54
2.26
Tl
2.16
4.01
9.09
9.5
5.39
11.8
12.1
11.9
Pb
35.4
27.9
2.67
3.47
17
2.92
1.64
2.69
Bi
2.94
1.39
1.16
1.26
4.48
1.38
0.66
0.88
Th
21.1
24.2
0.56
0.65
5.11
0.82
0.67
0.55
U
5.44
4.88
2.68
3.8
4.52
4.2
2.26
7.66
Nb
13
13.5
41.7
58.6
25.7
63.2
59.3
63
Ta
3.12
2.68
25.7
31.5
11.7
38.8
29.6
38.4
Zr
104
109
20
21.4
39.8
26
15.9
21.9
Hf
3.93
4.32
1.9
1.9
1.91
3.08
1.73
2.31
Sn
30.1
33.1
77.8
84.3
114
76.4
92.3
94
Sb
0.06
0.1
0.09
0.08
0.08
0.05
0.08
0.09
续表2
Continued Table 2
组分
黑云母二长花岗岩
二云母碱长花岗岩
锂(白)云母碱长花岗岩
黄玉-锂云母碱长花岗岩
SZL-1
SZL-2
SZL-3
SZL-4
SZL-5
SZL-6
SZL-7
SZL-8
Ti
1262
1459
76
71.9
549
140
44.5
46
W
10.2
11.5
15.8
15.9
13.8
19.1
19.3
19
As
1.08
1.11
1.63
1.24
1.49
1.1
1.15
1.03
V
13.4
14
0.93
0.79
4.99
1.57
0.62
0.49
La
27.2
32
0.8
0.66
7.62
1.12
0.44
0.37
Ce
58.5
65.3
1.05
0.84
15.7
1.31
0.86
0.72
Pr
6.73
7.79
0.23
0.19
1.88
0.32
0.12
0.1
Nd
22.9
26.7
0.9
0.78
6.68
1.24
0.34
0.31
Sm
4.65
5.51
0.33
0.25
1.7
0.3
0.16
0.12
Eu
0.48
0.6
<0.05
<0.05
0.21
<0.05
<0.05
<0.05
Gd
3.42
3.96
0.32
0.25
1.47
0.22
0.16
0.14
Tb
0.46
0.51
0.06
<0.05
0.26
<0.05
<0.05
<0.05
Dy
2.01
2.04
0.29
0.23
1.15
0.21
0.22
0.18
Ho
0.29
0.29
<0.05
<0.05
0.14
<0.05
<0.05
<0.05
Er
0.73
0.73
0.09
0.09
0.32
0.07
<0.05
0.05
Tm
0.1
0.1
<0.05
<0.05
<0.05
<0.05
<0.05
<0.05
Yb
0.64
0.62
0.09
0.11
0.29
0.07
0.05
<0.05
Lu
0.09
0.09
<0.05
<0.05
<0.05
<0.05
<0.05
<0.05
Sc
3.47
3.62
0.4
0.44
2.45
0.52
0.37
0.4
Y
8.98
7.84
1.24
1.01
3.02
0.97
1.1
1.12
ΣREE
128.20
146.24
4.26
3.53
37.47
4.99
2.50
2.12
ΣLREE
120.46
137.90
3.34
2.75
33.79
4.32
1.95
1.65
ΣHREE
7.74
8.34
0.93
0.78
3.68
0.67
0.56
0.47
LREE/HREE
15.56
16.53
3.61
3.52
9.18
6.44
3.50
3.50
δEu
0.35
0.37
0.23
0.30
0.40
0.28
0.47
0.59
(La/Yb)N
28.65
34.80
5.99
4.05
17.72
10.79
5.93
9.98
注:*总和中不包括CO2和H2O+,低于检出限的按照检出限的一半计算。AKI=n(Na2O+K2O)/n(Al2O3);A/NK=n(Al2O3)/n(Na2O+K2O);A/CNK=n(Al2O3)/n(CaO+Na2O+K2O)。比值单位为1。
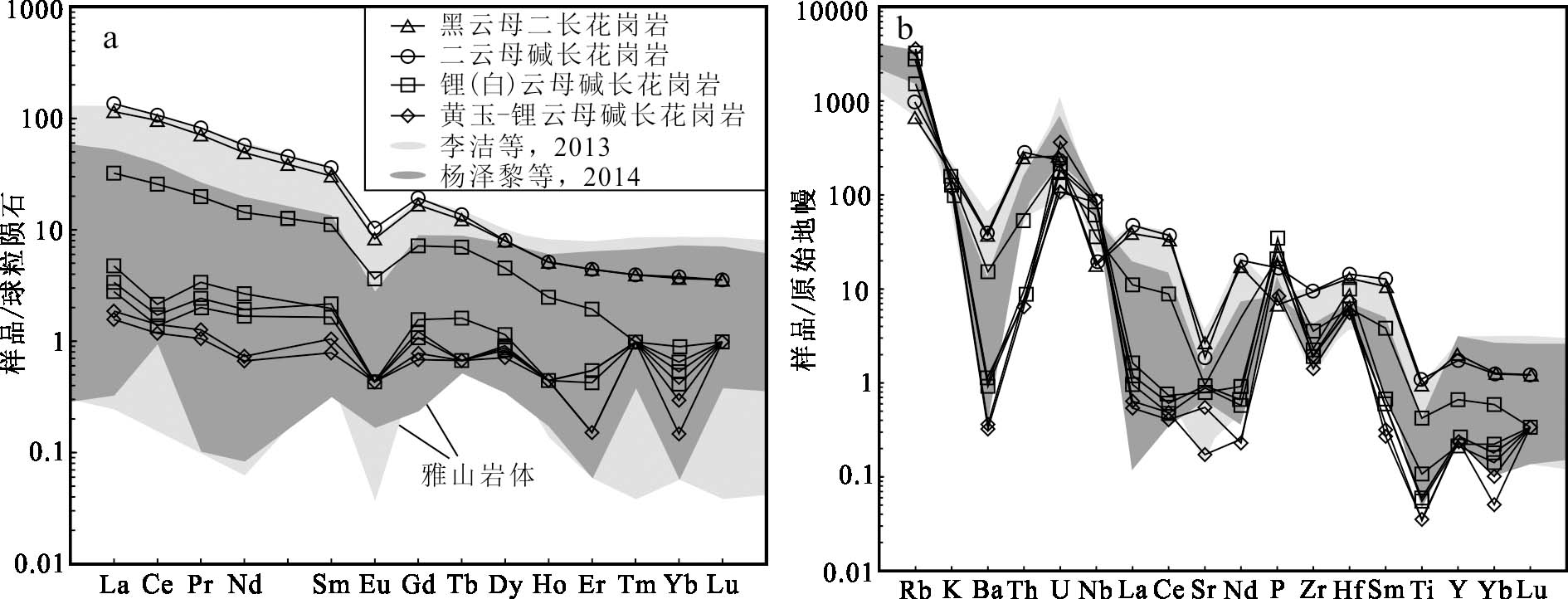
狮子岭矿化岩体稀土元素含量非常低,二云母碱长花岗岩具有最高的ΣREE值,也仅为146.24×10-6,略高于地壳ΣREE(125.15×10-6)(Rudnick et al.,2014)。狮子岭矿化岩体LREE(轻稀土元素)为1.65×10-6~137.9×10-6,HREE(重稀土元素)为0.47×10-6~8.34×10-6,LREE/HREE=3.50~16.53(低出检测限的元素含量按检测限的一半计算),(La/Yb)N比值为5.93~34.8,表明稀土元素具有中等分馏,轻稀土元素较重稀土元素富集。图6a显示矿化岩体具有弱到中等Eu负异常(δEu=0.23~0.59),锂(白)云母碱长花岗岩及黄玉-锂云母碱长花岗岩还表现出不同程度的Ce和Yb负异常。黑云母二长花岗岩稀土元素含量(ΣREE=128.2×10-6)与二云母碱长花岗岩相近,但明显高于演化程度更高的锂(白)云母碱长花岗岩及黄玉-锂云母碱长花岗岩。LREE/HREE=15.56,(La/Yb)N=28.65,δEu=0.35,表明黑云母二长花岗岩同样具有轻稀土元素富集的中等分馏及中等Eu负异常的特征。图6b显示黑云母二长花岗岩与矿化岩体均表现出富集Rb、U、P、Hf,亏损Ba、Sr、Zr、Ti等元素的特征,但是相较于矿化岩体,黑云母二长花岗岩更加富集U、Hf,亏损Sr元素。狮子岭岩体稀土及稀有元素表现出与雅山岩体相似的特征,均具有华南高演化花岗岩的普遍特征(图6,李洁等,2013;杨泽黎等,2014)。黑云母二长花岗岩中稀有元素Li、Rb、Cs含量较低,w(Li)、w(Rb)、w(Cs)分别为297×10-6、415×10-6和86.1×10-6。而矿化岩体中较晚阶段的锂(白)云母碱长花岗岩及黄玉-锂云母碱长花岗岩中稀有元素Li、Rb、Cs最为富集,w(Li)、w(Rb)、w(Cs)分别为1052×10-6~3325×10-6、969×10-6~2291×10-6和246×10-6~515×10-6(表2),表明狮子岭岩体Li等稀有金属成矿潜力巨大。
图5SiO2-(K2O+Na2O)图解(a)、A/NK-A/CNK图解(b)、SiO2-K2O图解(c)和SiO2-AR图解(d)(底图据Wright,1969;Maniar et al.,1989;Rickwood et al.,1989;Middlemost et al.,1994,图中黑色符号为本文资料,灰色符号为雅山岩体资料,据杨泽黎等,2014)
Fig.5SiO2-(K2O+Na2O)diagram(a), A/NK-A/CNK plot(b), SiO2-K2O plot(c) and SiO2-AR plot(d) (base maps are from Wright, 1969;Maniar et al., 1989; Rickwood et al., 1989; Middlemost et al., 1994, data of the black symbols are from this study, and those grey symbols for the Yashan granites, are quoted from Yang et al., 2014)
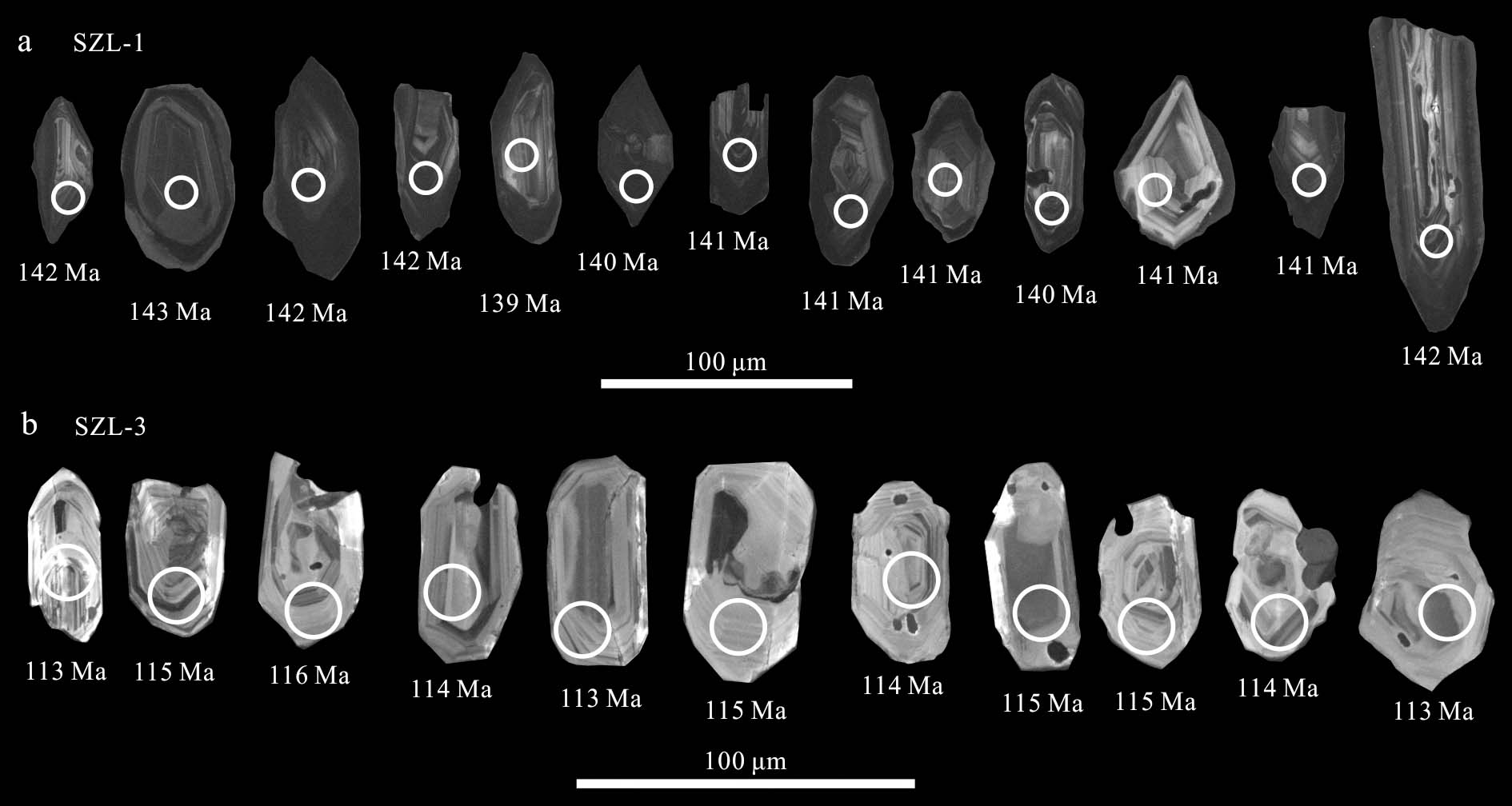
3.3锆石U-Pb测年结合锆石样品的透射光、反射光和阴极发光图像,尽量选择锆石颗粒表面无裂痕,内部环带清晰,无包裹体的锆石进行测年工作。本次实验共选择30个点进行分析,其中,24个点谐和度超过90%(表3)。
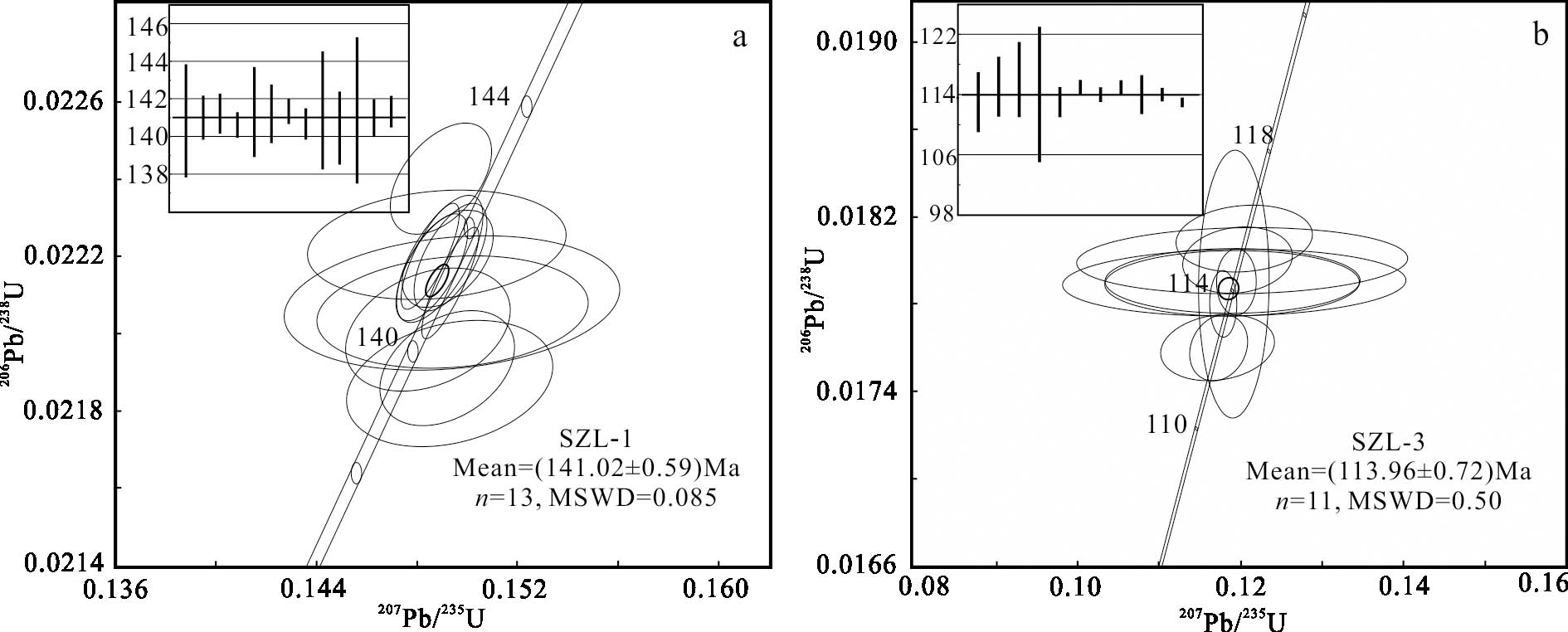
黑云母二长花岗岩(SZL-1)中的锆石CL图像显示大部分呈长柱状,长宽比在1.5~3.4之间,粒径在60~80 μm,少数小于50 μm或超过100 μm,可见明显震荡生长环带(图7a);测得锆石Th、U含量及比值分布范围非常大,w(Th)、w(U)分别为44×10-6~844×10-6和497×10-6~3167×10-6,Th/U比值范围在0.12~0.58之间,只有一个点Th/U比值为0.03,相对较低(表3)。YCSZL-3共测试分析13个点,13个测点谐和度均在96%以上。13颗锆石显示出较一致的206Pb/238U年龄,介于143~139 Ma之间,其加权平均年龄为(141.02±0.59)Ma(MSWD=0.085),代表黑云母二长花岗岩的成岩年龄(图8a)。
图6稀土元素球粒陨石标准化曲线(a)和微量元素原始地幔标准化曲线(b)(标准化数据取自Sun et al.,1989)
Fig.6Chondrite-normalized REE distribution patterns(a) and primitive-mantle-normalized trace element patterns(b) (normalized values after Sun et al., 1989)
锂(白)云母碱长花岗岩(SZL-3)中的锆石CL图像显示大部分晶型完整,呈短柱状,长宽比介于1.2~2.2之间,粒径在50~80 μm,仅有个别小于50 μm,可见明显震荡生长环带,为典型岩浆结晶锆石(图7b);测得的锆石Th、U含量比黑云母二长花岗岩较低,w(Th)、w(U)分别在92.9×10-6~281×10-6和81.3×10-6~161×10-6之间,Th/U比值范围在1.02~1.75之间(表3)。YCSZL-4共测试分析11个点,11个测点谐和度均超过99%。11颗锆石显示出较一致的206Pb/238U年龄,介于116~113 Ma之间,其加权平均年龄为(113.96±0.72)Ma(MSWD=0.50),代表锂(白)云母碱长花岗岩的成岩年龄(图8b)。
4讨 论4.1成岩成矿时代的限定赣西北是中国重要的稀有金属成矿区,区内稀有金属成矿作用受到燕山晚期岩浆活动影响。在燕山晚期发生多期次岩浆侵入事件,其中第一阶段第二次侵入活动为Li、Nb、Ta等稀有金属元素富集的高峰期(周建廷等,2011;吴学敏等,2016),形成一系列具有相似成矿过程的稀有金属矿床,如白水洞锂铌钽矿、茜坑锂矿、宜春414铌钽矿等以及近年新发现的存在大量富锂云母的大湖塘钨多金属矿。前人利用不同测试方法对该地区岩体及稀有金属矿床进行过详细的年代学研究,获得了大量年代学数据(表4)。如雅山岩体黄玉-锂云母花岗岩铌钽铁矿U-Pb年龄为(158±2)Ma(Che et al.,2015),二云母花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄为(155.88±0.60)Ma(李胜虎,2015);大湖塘钨矿区黑云母花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄为(151.3±2.8)Ma(Wei et al.,2018),石英脉型钨矿石辉钼矿Re-Os年龄为(137.9±2.0)Ma(张勇等,2017;2020),二云母花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄为(130.3±1.1)Ma(Huang et al.,2014);茜坑锂矿区锂云母花岗岩锂云母Ar-Ar年龄为(139.09±0.56)Ma(聂晓亮等,2022);白水洞锂铌钽矿区锂云母花岗岩铌钽铁矿U-Pb年龄为(144±5)Ma(Xie et al.,2019);东槽矿区白云母花岗岩锡石U-Pb年龄为(139.7±6.7)Ma(Ouyang et al.,2023);松树岗矿区黑云母花岗岩铌钽铁矿U-Pb年龄为(128±2)Ma(刘涛,2023)。由上述分析可得出赣西北地区稀有金属成岩成矿时间为160~130 Ma。本文获得狮子岭黑云母二长花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄为(141.02±0.59)Ma,属早白垩世早期岩体,这与赣西北地区成岩成矿时间一致,锂(白)云母碱长花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄为(113.96±0.72)Ma,由于磷锂铝石及锂云母等锂矿物可列为造岩矿物,所以成岩与稀有金属成矿同时发生,锂(白)云母碱长花岗岩成岩年龄可视为锂等稀有金属成矿年龄。狮子岭岩体稀有金属成矿时代晚于赣西北地区稀有金属主成矿期,在时间上与燕山晚期第一阶段第二次侵入活动末期一致(周建廷等,2011)。
表3江西宜丰狮子岭岩体的锆石同位素测年结果
Table 3 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating results of zircons from the Shiziling granites in Yifeng, Jiangxi
分析号
w(B)/10-6
Th/U
同位素比值及误差
年龄及误差/Ma
Pb
Th
U
207Pb/206pb
1σ
207Pb/235U
1σ
206Pb/238U
1σ
207Pb/206pb
1σ
207Pb/235U
1σ
206Pb/238U
1σ
黑云母二长花岗岩(n=13)
SZL-1-1
22
284
912
0.31
0.0483
0.0010
0.1488
0.0034
0.0222
0.0001
122
48
141
3
142
1
SZL-1-2
27
44
1713
0.03
0.0482
0.0003
0.1490
0.0013
0.0224
0.0001
109
12
141
1
143
1
SZL-1-3
40
271
2264
0.12
0.0488
0.0003
0.1492
0.0012
0.0222
0.0001
200
17
141
1
142
1
SZL-1-4
50
661
2179
0.30
0.0485
0.0001
0.1485
0.0008
0.0222
0.0001
124
6
141
1
142
1
SZL-1-5
23
387
885
0.44
0.0494
0.0008
0.1493
0.0027
0.0219
0.0001
169
40
141
2
139
1
SZL-1-6
57
844
2396
0.35
0.0494
0.0005
0.1492
0.0018
0.0219
0.0001
165
22
141
2
140
1
SZL-1-7
55
368
3167
0.12
0.0490
0.0001
0.1493
0.0008
0.0221
0.0001
146
4
141
1
141
1
SZL-1-8
43
421
2183
0.19
0.0486
0.0002
0.1486
0.0009
0.0222
0.0001
132
9
141
1
141
1
SZL-1-9
20
250
925
0.27
0.0491
0.0011
0.1494
0.0036
0.0221
0.0001
154
54
141
3
141
1
SZL-1-10
34
316
1806
0.17
0.0489
0.0005
0.1484
0.0022
0.0220
0.0001
143
23
141
2
140
1
SZL-1-11
15
287
497
0.58
0.0488
0.0012
0.1494
0.0044
0.0221
0.0001
139
59
141
4
141
1
SZL-1-12
19
293
789
0.37
0.0487
0.0002
0.1489
0.0011
0.0222
0.0001
132
11
141
1
141
1
SZL-1-13
34
399
1576
0.25
0.0488
0.0002
0.1493
0.0010
0.0222
0.0001
139
7
141
1
142
1
锂(白)云母碱长花岗岩(n=11)
SZL-3-1
5
223
137
1.63
0.0480
0.0017
0.1172
0.0046
0.0176
0.0001
102
85
113
4
113
1
SZL-3-2
5
186
152
1.22
0.0480
0.0016
0.1196
0.0044
0.0180
0.0001
98
78
115
4
115
1
SZL-3-3
4
140
131
1.07
0.0476
0.0018
0.1205
0.0055
0.0181
0.0001
76
89
116
5
116
1
SZL-3-4
7
281
161
1.75
0.0467
0.0033
0.1190
0.0103
0.0179
0.0001
32
163
114
9
114
1
SZL-3-5
3
114
91
1.26
0.0482
0.0009
0.1173
0.0023
0.0176
0.0001
109
43
113
2
113
0
SZL-3-6
5
167
145
1.15
0.0453
0.0039
0.1202
0.0134
0.018
0.0001
98
211
115
1
115
1
SZL-3-7
5
191
137
1.39
0.0444
0.0043
0.1192
0.0139
0.0179
0.0001
98
204
114
1
114
1
SZL-3-8
4
131
113
1.16
0.0481
0.0012
0.1195
0.0016
0.0179
0.0001
106
53
115
1
115
1
SZL-3-9
4
116
114
1.02
0.0465
0.0031
0.1192
0.0029
0.0179
0.0004
33
156
114
3
115
2
SZL-3-10
3
92.9
86.3
1.08
0.0454
0.0037
0.1189
0.0103
0.0179
0.0001
100
157
114
1
114
1
SZL-3-11
3
99.9
81.3
1.23
0.0456
0.0076
0.1179
0.0011
0.0178
0.0001
122
139
113
1
113
1
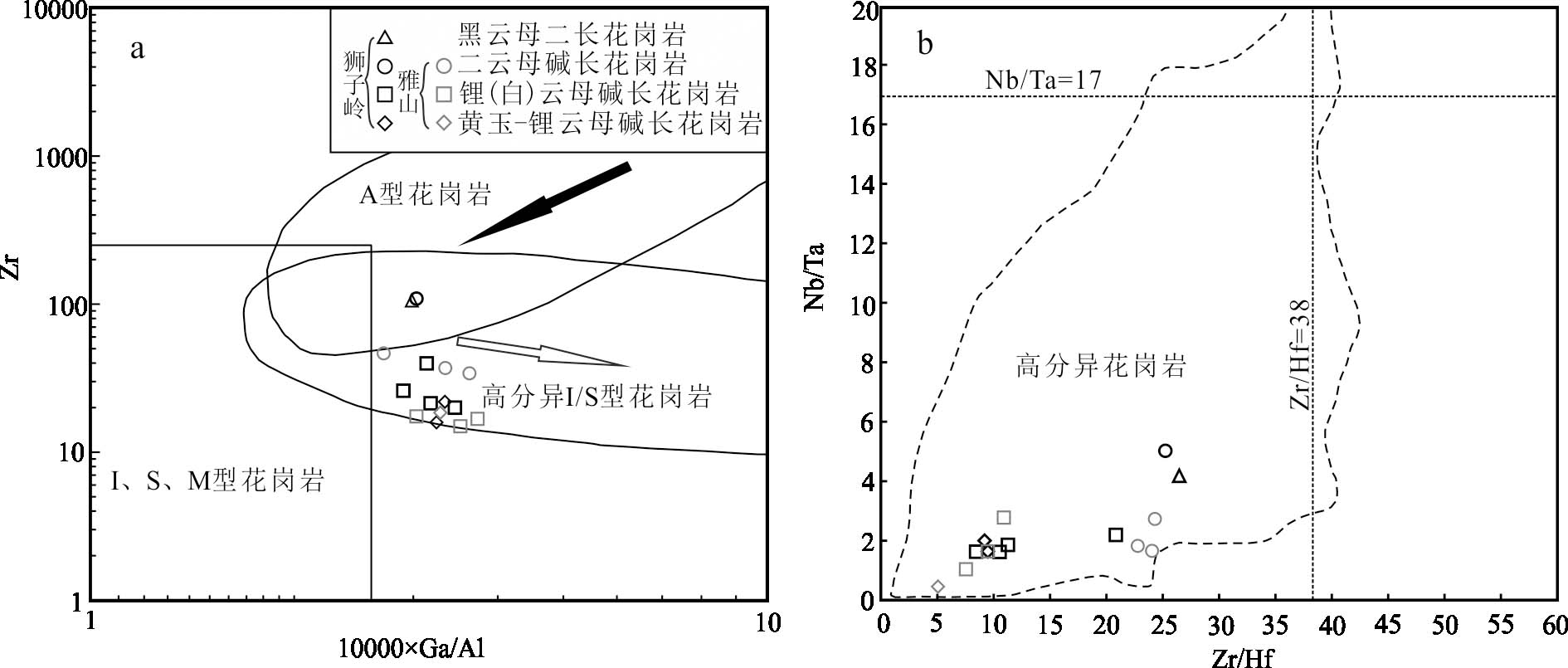
4.2狮子岭岩体成因类型前文中提到狮子岭岩体的分异指数(DI)平均值90.81,此外在10000×Ga/Al-Zr及Nb/Ta-Zr/Hf图解(图9)中,狮子岭岩体同样显示了高分异花岗岩的特征。由于高分异的S型花岗岩与A型花岗岩的某些地球化学特征相似,因此,在判断这类花岗岩成因类型时需要多方面的证据。秦程(2018)对狮子岭锂(白)云母碱长花岗岩进行研究时发现其10000×Ga/Al比值较高,按Whalen等(1987)基于Ga/Al比值提出的花岗岩成因类型标准,可以归属为A型花岗岩。但是笔者认为除此比值外,缺少其他能够限制其成因类型为A型花岗岩的证据。此外,有学者认为与A型花岗岩相比,高分异的S型花岗岩同样可以具有较高的10000×Ga/Al比值(如高于2.6),富含高场强元素(HFSEs)(Li et al.,2007;Wu et al.,2017)。
本文所采集的狮子岭岩体样品在地球化学特征上与S型花岗岩有较强的相似性。如I、A型花岗岩的A/CNK值一般在1.0~1.1之间,为弱过铝质花岗岩,S型花岗岩A/CNK值一般大于1.1,而狮子岭岩体样品A/CNK值最小为1.32,均属于强过铝质花岗岩,因此其A/CNK值指示狮子岭岩体与S型花岗岩具有更近的亲缘性;I、A型花岗岩P2O5含量很低,仅有0.1%,且随着岩浆演化而降低(Harrison et al.,1984),强过铝质S型花岗岩P2O5含量会随A/CNK值增大而增加(Wolf et al.,1994),而狮子岭岩体富磷,P2O5含量随着分异演化程度逐渐增加,其A/CNK值越大,P2O5含量越高,这一特征也与S型花岗岩更为相近;A型花岗岩除Eu亏损外,其余稀土元素含量均较高,且A型花岗岩过碱指数(AKI值)一般大于0.85(Whalen et al.,1987),而狮子岭岩体具有较低的稀土元素含量及相对偏低的碱含量(0.48~0.71),这指示其具有更偏向S型花岗岩的地球化学特征;吴福元等(2023)认为判定高分异花岗岩成因类型最可行的办法是看同时代岩石的成因类型。前文提到的大湖塘花岗岩、茜坑花岗岩、雅山岩体的地球化学特征与S型花岗岩相似(Huang et al.,2014;杨泽黎等,2014;Wei et al.,2018;聂晓亮等,2022),且同狮子岭岩体均为燕山晚期第一阶段岩浆侵入的产物。综上所述,笔者认为狮子岭岩体应为高分异的S型花岗岩,而非前人认为的A型花岗岩。
表4赣西北地区花岗岩成岩及稀有金属成矿年龄统计
Table 4 Petrogenic and rare metal mineralization ages of granite complex in northwestern Jiangxi
岩性
测试方法
年龄/Ma
资料来源
狮子岭岩体
黑云母二长花岗岩
LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb
141.02±0.59
本文
锂(白)云母碱长花岗岩
LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb
113.96±0.72
本文
大湖塘矿区
黑云母花岗斑岩
LA-ICP-MS锡石U-Pb
153±25
潘大鹏等,2017
黑云母花岗斑岩
LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb
147.7±1.5
潘大鹏等,2017
黑云母花岗岩
LA-ICP-MS锡石U-Pb
148.7±8.8
潘大鹏等,2017
黑云母花岗岩
LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb
151.3±2.8
Wei et al.,2018
细粒花岗岩
LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb
150.1±1.2
Wei et al.,2018
含矿花岗斑岩
LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb
142.7±2.3
Wei et al.,2018
石英脉型矿石
辉钼矿Re-Os
137.9±2
张勇等,2017
白云母花岗岩
LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb
144.2±1.3
黄兰椿等,2012
白云母花岗岩
LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb
133.7±0.5
Huang et al.,2014
二云母花岗岩
LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb
130.3±1.1
Huang et al.,2014
二云母花岗岩
LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb
130.7±1.1
Huang et al.,2014
茜坑矿区
锂云母花岗岩
锂云母Ar-Ar
139.09±0.56
聂晓亮等,2022
白水洞矿区
锂(白)云母花岗岩
LA-ICP-MS铌钽铁矿U-Pb
144±5
Xie et al.,2019
白云母花岗岩
LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb
146.3±1.08
姜宝亮等,2022
东槽矿区
白云母花岗岩
LA-ICP-MS锡石U-Pb
139.7±6.7
Ouyang et al.,2023
松树岗矿区
黑云母花岗岩
LA-ICP-MS铌钽铁矿U-Pb
128±2
刘涛,2023
雅山岩体
二长花岗岩
SHRIMP锆石U-Pb
161.5±1.8
Li et al.,2018
黑云母花岗闪长岩
TIMS锆石U-Pb
161±1
楼法生等,2005
黄玉-锂云母花岗岩
LA-ICP-MS铌钽铁矿U-Pb
160±1
Che et al.,2015
白云母花岗岩
LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb
156±0.4
左梦璐,2016
二云母花岗岩
LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb
150.1±1
杨泽黎等,2014
二云母花岗岩
LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb
155.88±0.6
李胜虎,2015
锂云母花岗岩
LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb
150.2±1.4
杨泽黎等,2014
锂云母钠长石花岗岩
辉钼矿Re-Os
152.54±0.8
李胜虎,2015
4.3岩浆演化与稀有金属成矿狮子岭未发生稀有金属矿化的黑云母二长花岗岩成岩时代为早白垩世早期,发生矿化的锂(白)云母碱长花岗岩成岩时代为早白垩世晚期,成岩时间上相差近30 Ma,推测二者是不同期次岩浆侵入后结晶分异形成。黑云母二长花岗岩在矿物组成上,并未见较为富Li、Nb、Ta的矿物,笔者认为该期次岩浆对狮子岭稀有金属成矿贡献不大。前人研究指出,赣西北地区稀有金属成矿通常与富氟花岗岩密切相关,又可根据P2O5含量划分出高磷亚型和低磷亚型,其中的高磷亚型以w(SiO2)<73%、w(Al2O3)>14%和低稀土元素为特征,一般除经历早期的岩浆结晶分异演化外,还有晚期的熔体-流体相互作用(李福春等,2000;黄小龙等,2001;李洁,2015)。此外,有学者认为以Zr/Hf=26和Nb/Ta=5为界,可将过铝质花岗岩划分出典型的结晶分异成因和岩浆-热液相互作用成因(Bau et al.,1996;Ballouard et al.,2016)。狮子岭矿化岩体w(SiO2)平均为71.54%、w(Al2O3)平均为16.7%、低稀土元素(平均28.73×10-6)、低Nb/Ta(1.62~5.03)和Zr/Hf(8.44~25.23)比值(表1),这些地球化学特征表明狮子岭矿化岩体除了经历岩浆的高度结晶分异外,可能在演化晚期经历了熔体-流体相互作用,与雅山岩体和大湖塘燕山期花岗岩具有相似的岩浆演化过程(李洁等,2013;杨泽黎等,2014;张勇等,2017;Yin et al.,2022)。
图7狮子岭地区黑云母二长花岗岩(a)、锂(白)云母碱长花岗岩(b)锆石阴极发光图像及测点位置与结果
Fig.7CL images, site of analyzed points and dating data of zircons from biotite monzogranite(a), lepidolite (muscovite) alkali feldspar granite(b) in Shiziling
图8狮子岭地区黑云母二长花岗岩(a)、锂(白)云母碱长花岗岩(b)锆石U-Pb年龄谐和图及加权平均年龄
Fig.8Zircon U-Pb concordia diagrams and weighted average ages for zircons in biotite monzogranite (a) and lepidolite (muscovite) alkali feldspar granite (b) from Shiziling granites
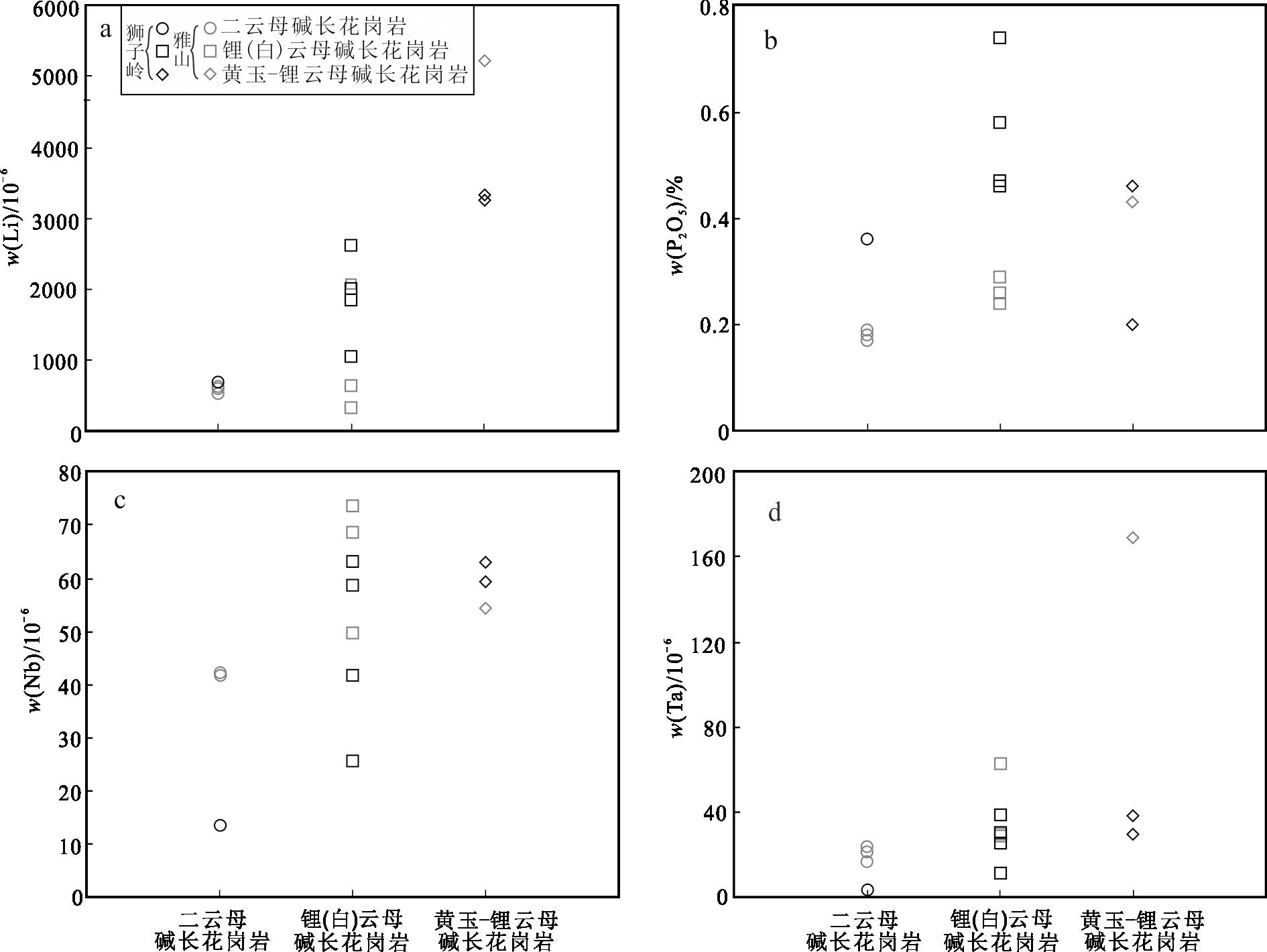
狮子岭矿化岩体从早期的二云母碱长花岗岩到晚期的黄玉-锂云母碱长花岗岩,岩浆演化程度不断升高,体系内的Li、F、P等不断富集。Li具有类似于非碱金属元素的地球化学特征,使其倾向于富集在花岗质岩浆结晶晚期的残余熔体或岩浆期后的热液中(Černý et al.,1985)。岩浆演化过程中Li元素富集会改变花岗质岩浆体系的结晶温度,从而延长结晶时间,促进岩浆的结晶分异作用(Brookins,1986)。岩浆中F和P元素的存在可以降低熔体的粘度和固相线温度,加速晶体-熔体之间的分离,同样可以促进岩浆高度分异演化(Mysen et al.,1981;London et al.,1993;李建康等,2008)。磷锂铝石和锂云母等稀有金属矿物及黄玉、萤石等副矿物作为Li、F、P主要的赋存矿物,会在岩浆演化后期逐渐结晶析出。Nb、Ta元素在强过铝质熔体中为不相容元素,在岩浆-热液过渡阶段发生的熔体-流体相互作用过程中,Nb、Ta的流体/熔体分配系数极低,因此在岩浆演化过程中倾向于进入晚期形成的熔体相(Linnen et al.,2005;Keppler,1996;Chevychelov et al.,2004)。岩浆演化晚期体系内富集的Li、F、P等挥发分可以改变硅酸盐的结构,破坏硅酸盐的成网离子,导致碱金属离子由“成网离子”变为“变网离子”,使体系内非氧桥(NBO)数逐渐增加(Mysen et al.,1981;Linnen et al.,1988;Horng et al.,1999)。熔体中的非氧桥数增加将使Nb、Ta等金属阳离子元素在铝硅酸盐中的溶解度增大(Van Lichtervelde et al.,2010),导致Nb、Ta等元素在矿化岩体中富集而形成铌钽氧化物(铌铁矿族矿物、细晶石及含钽锡石)。狮子岭矿化岩体与雅山岩体具有相似的岩浆演化特征,从早阶段到晚阶段的花岗岩样品中,Li、P2O5及Nb、Ta逐渐富集,较晚阶段的锂(白)云母碱长花岗岩及黄玉-锂云母碱长花岗岩具有非常高的w(Li),w(P2O5)及w(Nb)、w(Ta)(图10a~d)。以上元素地球化学特征表明,Li、Nb、Ta元素的富集成矿与狮子岭地区岩浆高度结晶分异密切相关。
图9狮子岭岩体及雅山岩体10000×Ga/Al-Zr图解(a)及Nb/Ta-Zr/Hf图解(b)(底图据Wu et al.,2017,图中黑色符号为本文资料;灰色符号为雅山岩体资料,据杨泽黎等,2014)
Fig.9 10000×Ga/Al-Zr diagram (a) and Nb/Ta-Zr/Hf diagram of Shiziling granites and Yashan granites (b) (base map are from Wu et al., 2017, data of the black symbols are from this study and those grey symbols for the Yashan granites are quoted from Yang et al., 2014)
锂云母、磷锂铝石、富钽锡石等矿物的结晶析出,代表狮子岭地区岩浆经历了高度结晶分异演化(王成辉等,2018;2019;刘泽等,2023)。随着岩浆的持续演化,在岩浆-热液过渡阶段过程中,狮子岭矿化岩体还经历了钠长石化、锂化(黑鳞云母化、锂云母化、锂白云母化)及氟硅化(硅化、黄玉化)等交代作用。二云母碱长花岗岩中可见由原生自形片状黑云母蚀变形成的黑鳞云母交代穿切岩浆结晶成因白云母(图4a)。锂(白)云母碱长花岗岩及黄玉-锂云母碱长花岗岩中,可见晚期钠长石和锂云母沿着钾长石、石英的边部或内部裂隙进行交代(图4f、g),晚期钠长石交代穿切早期结晶成因锂云母。本文研究的狮子岭矿化岩体样品中除出现岩浆结晶分异作用形成的大颗粒磷锂铝石(粒径200~500 μm,图4c)外,还发现岩浆-热液过渡阶段经交代作用形成的磷锂铝石蚀变边(粒径20~80 μm,图4d),可能为岩浆结晶成因的磷锂铝石经交代作用后破碎而形成,为交代残余产物。造成狮子岭岩体锂化蚀变的热液流体,可能就是岩浆-热液过渡阶段高度富集Li、F、K的碱性流体,这个阶段的锂元素主要富集在热液成因的云母(黑鳞云母、锂云母)、磷锂铝石中。岩浆-热液过渡阶段经交代形成的锂云母等锂矿物,其粒度和含量都远小于岩浆结晶分异过程中形成的,因此,笔者认为该阶段对Li矿化的贡献较岩浆结晶分异小一些。有学者提出,云母形成和后期热液交代保留了有关花岗岩成岩作用和热液过程的微量元素变化及Li等稀有金属富集的特征(Zhu et al.,2019;Monnier et al.,2022)。Xu等(2023)以Nb/Ta、Zr/Hf比值及F值为依据将狮子岭-白水洞地区及宜春414铌钽矿中白云母花岗岩中的云母划分出不同阶段,发现后期热液交代成因锂云母中的Li含量高于交代再平衡云母和岩浆结晶成因的原生白云母,这表明狮子岭地区岩浆-热液过渡阶段发生的交代作用在岩浆结晶分异的基础上再度富集Li等成矿元素。
图10狮子岭矿化岩体及雅山岩体不同阶段花岗岩的w(Li)(a)、w(P2O5)(b)、w(Nb)(c)、w(Ta)(d)(图中黑色符号为本文资料,灰色符号为雅山岩体资料,据杨泽黎等,2014)
Fig.10w(Li) (a),w(P2O5) (b),w(Nb) (c), andw(Ta) (d) in three units of the Shiziling mineralized granites and Yashan granites (data of the black symbols are from this study and those grey symbols for the Yashan granites are quoted from Yang et al., 2014)
综上所述,笔者认为尽管狮子岭矿化岩体稀有金属元素富集成矿受到岩浆的结晶分异演化和岩浆-热液过渡阶段发生的交代蚀变作用共同影响,但岩浆的结晶分异演化对Li、Nb、Ta成矿元素的高度富集起决定性作用,而后期岩浆-热液过渡阶段发生的交代蚀变作用为Li等成矿元素的二次富集提供了条件。
5结 论
(1) 赣西北狮子岭黑云母二长花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄为(141.02±0.59)Ma,成岩作用发生于早白垩世早期;锂(白)云母碱长花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄为(113.96±0.72)Ma,成岩与稀有金属成矿同时发生于早白垩世晚期。
(2) 狮子岭地区矿化花岗岩属高钾钙碱性系列,具有高硅、富磷,富U、Hf等高场强元素和稀土元素含量低的特点,具有弱到中等Eu负异常,整体上表现出典型S型花岗岩的地球化学特征。
(3) 狮子岭地区稀有金属矿化受燕山晚期岩浆结晶分异作用及后期热液交代作用的共同影响。岩浆高度结晶分异对Li、Nb、Ta元素的高度富集和最终矿化至关重要,后期发生的热液交代作用在岩浆结晶分异的基础上再度富集Li等成矿元素。
(4) 赣西北地区晚侏罗世—早白垩世高分异花岗岩与锂等稀有金属成矿关系密切,在该时期形成的岩体内部具有寻找锂矿资源的巨大潜力。
致 谢 匿名审稿专家和编辑对本文提出了许多有益的修改意见,在此表示由衷的感谢!
-
参考文献
Ballouard C, Poujol M, Boulvais P, Branquet Y, Tartese R and Vigneresse J L. 2016. Nb-Ta fractionation in peraluminous granites: A marker of the magmatic-hydrothermal transition[J]. Geology, 44(3): 231-234.
Bau M. 1996. Controls on the fractionation of isovalent trace elements in magmatic and aqueous systems: Evidence from Y/Ho, Zr/Hf, and lanthanide tetrad effect[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 123: 323-333.
Brookins D G. 1986. Natural analogues for radwaste disposal: Elemental migration in igneous contact zones[J]. Chemical Geology, 55(3-4): 337-344.
Černý P and Ercit T S. 1985. Some recent advances in the mineralogy and geochemistry of Nb and Ta in rare-element granitic pegmatites[J]. Bulletin de Minéralogie, 108(3): 499-532.
Che X D, Wu F Y, Wang R C, Gerdes A, Ji W Q, Zhao Z H, Yang J H and Zhu Z Y. 2015. In situ U-Pb isotopic dating of columbite-tantalite by LA-ICP-MS[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 65(4): 979-989.
Chevychelov V, Zaraisky C, Borisovskiy S Y and Borkov D. 2004. Partitioning of Ta and Nb between magmatic melt and aqueous (K,Na,H)F-containing fluid. Effects of temperature and chemical composition of the melt[J]. lithos, 73(1-2):17.
Duan Z, Liao S B, Chu P L, Huang W C, Zhu Y H, Shu X J and Li C B. 2019. Zircon U-Pb ages of the Neoproterozoic Jiuling complex granitoid in the eastern segment of the Jiangnan orogen and its tectonic significance[J]. Geology in China, 46(3): 493-516(in Chinese with English abstract).
Harrison T M and Waston E B. 1984. The behavior of apatite during crustal anatexis: Equilibrium and kinetic considerations[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 48(7): 1467-1477.
Horng W S, Hess P C and Gan H. 1999. The interactions between M+5 cations (Nb+5, Ta+5, or P+5) and anhydrous haplogranite melts[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 63(16): 2419-2428.
Hou K J, Li Y H and Tian Y R. 2009. In situ U-Pb zircon dating using laser ablation-multiion counting-ICP-MS[J]. Mineral Deposits, 28(4): 481-492(in Chinese with English abstract).
Huang L C and Jiang S Y. 2012. Zircon U-Pb geochronology, geochemistry and petrogenesis of the porphyric-like muscovite granite in the Dahutang tungsten deposit, Jiangxi Province[J]. Acta Petrolo-gica Sinica, 28(12): 3887-3900(in Chinese with English abstract).
Huang L C and Jiang S Y. 2014. Highly fractionated S-type granites from the giant Dahutang tungsten deposit in Jiangnan Orogen, Southeast China: Geochronology, petrogenesis and their relationship with W-mineralization[J]. Lithos, 202-203: 207-226.
Huang X L, Wang R C, Chen X M and Liu C S. 2001. Phosphate mi-nerals from the Yashan F and P-rich granite in Yichun, Jiangxi Province: Genetic implications[J]. Geological Review, 47(5): 542-550(in Chinese with English abstract).
Jiang B L, Zhao J, Lin M H and Zhang L. 2022. Zircon U-Pb age of ore-forming magmatic rocks in Baishuidong lithium niobium tantalum deposit, Yifeng County, Jiangxi Province and its significance[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, (19): 73-75(in Chinese with English abstract).
Keppler H. 1996. Constraints from partitioning experiments on the composition of subduction-zone fluids[J]. Nature, 380: 237-240.
Li F C, Zhu J C and Jin Z D. 2000. Genetic interpretation of Li-F-rich rare metal-bearing granites in South China[J]. Mineral Deposits, 19(4): 376-385(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li J and Huang X L. 2013. Mechanism of Ta-Nb enrichment and magmatic evolution in the Yashan granites, Jiangxi Province, South China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(12): 4311-4322(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li J. 2015. Mineralogical constraints on magmatic and hydrothermal evolutions of the Mesozoic rare-metal granites in South China[D]. Supervisor: Huang X Y. Guangzhou: Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry. 1-122(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li J K, Zhang D H, Wang D H and Zhang W Z. 2008. Liquid immiscibility of fluorine rich granite magma and its diagenesis and metallogeny[J]. Geological Review, 54(2): 175-183.
Li J K, Liu X F and Wang D H. 2014. The metallogenetic regularity of lithium deposit in China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 88(12): 2269-2283(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li J K, Li P and Chen Z Y. 2023. Metallogenic regularity, prediction and assessment of strategic metal mineral resources such aslithium and beryllium: Preface[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 39(7): 1881-1886(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li S H. 2015. Ore-forming mechanisms and prospecting models of typical granite type rare metal deposits in South China[D]. Supervisor: Zhang D H and Li J K. Beijing: China University of Geosciences. 1-178(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li X F, Yi X K, Cheng H, Wang C Z, Wei X L, Zhu Y T and Xu J. 2018. Zircon U-Pb, molybdenite Re-Os and muscovite Ar-Ar geochronology of the Yashan W-Mo and Xiatongling W-Mo-Be deposits: Insights for the duration and cooling history of magmatism and mineralization in the Wugongshan district, Jiangxi, South China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 102: 1-17.
Li X H, Li Z X, Ge W C, Zhou H W, Li W X, Liu Y and Wingate M. 2003. Neoproterozoic granitoids in South China: Crustal melting above a mantle plume at ca. 825 Ma[J]? Precambrian Research, 122(1): 45-38.
Li X H, Li Z X, Li W X, Liu Y, Yuan C, Wei G J and Qi C. 2007. U-Pb zircon, geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic constraints on age and origin of Jurassic I- and A-type granites from central Guangdong, SE China: A major igneous event in response to foundering of a subducted flat-slab[J]? Lithos, 96(1-2): 186-204.
Linnen R L. 1998. The solubility of Nb-Ta-Zr-Hf-W in granitic melts with Li and Li + F; constraints for mineralization in rare metal granites and pegmatites[J]. Econ. Geol., 93(7): 1013-1025.
Linnen R L and Cuney M. 2005. Granite-related rare-element deposits and experimental constraints on Ta-Nb-W-Sn-Zr-Hf mineralization[A]. In: Linnen R L and Samson I M, eds. Rare-element geochemistry and mineral deposits[C]. Geological Association of Canada, GAC Short Course Notes, 17: 45-67.
Liu T. 2023. Magmatic-hydrothermal evolution and Nb-Ta mineralization in the Lingshan complex, Southeast China[D]. Supervisor: Jiang S Y. Beijing: China University of Geosciences. 43-44(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Z, Chen Z Y and Wang C H. 2023. mineralogical characteristics and metallogenic mechanism of Shiziling Li-Ta deposit in Northwest Jiangxi[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 39(7): 2045-2062(in Chinese with English abstract).
London D, Morgan G B, Babb H A and Loomis J L. 1993. Behavior and effects of phosphorus in the system Na2O-K2O-Al2O3-SiO2-P2O5-H2O at 200 MPa(H2O)[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 113(4): 450-465.
Lou F S, Shen W Z, Wang D Z, Shu L S, Wu F J, Zhang F R and Yu J H. 2005. Zircon U-Pb isotopic chronology of the Wugongshan dome compound granite in Jiangxi Province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 79(5): 636-644(in Chinese with English abstract).
Ludwig K R. 2003. Users manual for Isoplot/Ex: A geochronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel[J]. Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication, 4: 1-71.
Maniar P D and Piccoli P M. 1989. Tectonic discrimination of grani-toids[J]. The Geological Society of America Bulletin, 101(5): 635-643.
Middlemost E A K. 1994. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 37(3): 215-224.
Monnier L, Salvi S, Melleton J, Lach P, Pochon A, Bailly L, beziat D and Parseval P D. 2022. Mica trace-element signatures: Highligh-ting superimposed W-Sn mineralizations and fluid sources[J]. Chemical Geology, 600(1): 120866.
Mysen B O, Ryerson F J and Virgo D. 1981. The structural role of phosphorus in silicate melts[J]. American Mineralogist, 66(1-2): 106-117.
Nie X L, Wang S L, Liu S and Xu L. 2022. Geological and geochemical characteristics of the Xikeng lithium deposit and the 40Ar/39Ar chronology of lepidolite of the deposit in Jiangxi Province, China[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 42(3): 285-294(in Chinese with English abstract).
Ouyang Y P, Zeng R L, Meng D L, Li T F and Wei J. 2023. Geochronology and geochemistry characteristics of Dongcao muscovite granite in the Yifeng area, Jiangxi Province, China: Implications for petrogenesis and mineralization[J]. Minerals, 13(4): 503.
Pan D P, Wang D and Wang X L. 2017. Petrogenesis of granites in Shimensi in northwestern Jiangxi Province and its implications for tungsten deposits[J]. Geology in China, 44(1): 118-135(in Chinese with English abstract).
Qin C. 2018. Preliminary study of mineralization potentiality of Shizi-ling muscovite granite, Jiangxi Province[D]. Supervisor: Liu X F.Beijing: China University of Geosciences: 1-61(in Chinese with English abstract).
Rickwood P C. 1989. Boundary lines within petrologic diagrams which use oxides of major and minor elements[J]. Lithos, 22(4): 247-263.
Rudnick R L and Gao S. 2014. Composition of the continental crust[M]. Treatise on Geochemistry 4.1, p43.
Sun K K, Chen B, Chen J S and Xiang X K. 2017. The petrogenesis of the Jiuling granodiorite from the Dahutang deposit, Jiangxi Pro-vince and its tectonic implications[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 33(3): 907-924(in Chinese with English abstract).
Sun S S and McDonough W F. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systema-tics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications, 42(1): 313-345.
Sun Y, Wang C H, Guo M W, Wang D H, Yang Y Q, Fan X J and Chen L. 2018. Application prospect and occurrence of Li, Rb, Cs of Shiziling granite in Northwestern Jiangxi[A]. Proceedings of the 14th National Conference on Mineral Deposits[C]. 376-377(in Chinese).
Van Lichtervelde M, Holtz F and Hanchar J M. 2010. Solubility of manganotantalite, zircon and hafnon in highly fluxed peralkaline to peraluminous pegmatitic melts[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 160(1): 17-32.
Wang C H, Yang Y C, Wang D H, Sun Y, Chen Z Y, Xie G G and Fan X J. 2018. Discovery of amblygonite and Li-Be-Sn-Ta minerals in the Jiuling area, Jiangxi Province[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 37(1): 108-110(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang C H, Wang D H, Chen C, Liu S B, Chen Z Y, Sun Y, Zhao C H, Cao S H and Fan X J. 2019. Progress of research on the Shiziling rare metals mineralization from Jiuling-type rock and its significance for prospecting[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 93(6): 1359-1373(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang C H, Wang D H, Liu S B, Xu J X, Qin J H, Qin Y, Liu J Y, Zhao Z, Feng W J, Liu Z Q, Zhao Y Y and Guo C L. 2022. New disco-very and regional prospecting potentiality of greisen-type lithium mineralization in the Shilei tungsten and tin deposit,Southern Jiangxi Province[J]. Geology in China, 49(6): 1834-1844(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang D, Wang X L, Cai Y, Chen X, Zhang F R and Zhang F F. 2017. Heterogeneous conservation of zircon Xenocrysts in Late Jurassic granitic intrusions within the Neoproterozoic Jiuling Batholith, South China: A magma chamber growth model in deep crustal hot zones[J]. Journal of Petrology, 58(9): 1781-1810.
Wang D, Wang X L, Cai Y, Li J H, Du D H and Shu X J. 2022. Explo-ring the Sn-W metallogenic potential of Late Jurassic Ganfang-Guyangzhai granite suite, South China: Zircon and apatite geochemistry[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 144(6): 104863.
Wang D H, Liu S B, Yu Y, Wang C H, Sun Y, Dai H Z, Li J K, Dai J J, Wang Y X, Zhao T, Ma S S and Liu L J. 2019. Exploration progress and development suggestion for the large-scale mining base of strategic critical mineral sesources in western Sichuan[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 93(6): 1444-1453(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang X L, Zhou J C, Griffin W L, Zhao G C, Yu J H, Qiu J S, Zhang Y J and Xing G F. 2014. Geochemical zonation across a Neoproterozoic orogenic belt: Isotopic evidence from granitoids and metasedimentary rocks of the Jiangnan orogen, China[J]. Precambrian Research, 242(3): 54-171.
Wei W F, Shen N P, Yan B, Lai C K, Yang J H, Gao W and Liang F. 2018. Petrogenesis of ore-forming granites with implications for W-mineralization in the super-large Shimensi tungsten-dominated polymetallic deposit in northern Jiangxi Province, South China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 95: 1123-1139.
Whalen J B, Currie K L and Chappell B W. 1987. A-type granites: Geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 95(4): 407-419.
Wolf M B and London D. 1994. Apatite dissolution into peraluminous haplogranitic melts: An experimental study of solubilities and mechanisms[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 58(19): 4127-4145.
Wright J B. 1969. A simple alkalinity ratio and its application to questions of non-orogenic granite genesis[J]. Geological Magazine, 106: 307-384.
Wu F Y, Liu X C, Ji W Q, Wang J M and Yang L. 2017. Highly fractionated granites: Recognition and research[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 60(7): 1201-1219.
Wu F Y, Guo C L, Hu F Y, Liu X C, Zhao J X, Li X F and Qin K Z. 2023. Petrogenesis of the highly fractionated granites and their mineralizations in Nanling Range, South China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 39(1): 1-36(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wu X M, Zhou M J, Luo X C and Zhou J T. 2016. The metallogenic conditions and prospecting potential of lithium and rare metals in northwestern Jiangxi[J]. East China Geology, 37(4): 275-283(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xie L, Liu Y, Wang R C, Hu H, Che X D and Xiang L. 2019. Li-Nb-Ta mineralization in the Jurassic Yifeng granite-aplite intrusion within the Neoproterozoic Jiuling batholith, South China: A fluid-rich and quenching ore-forming process[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 185: 104047.
Xu Z, Zhang Y, Pan J Y, Zhang F S, Xia F, Wu Z C, Han S C, Liu G Q, Zhong F J, Zhan X T, Liu Y and Yan J. 2023. In situ LA-ICP-MS analyses of muscovite: Constraints on granite-type Li mineralization in northwestern Jiangxi, South China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 156: 105402.
Yang Y Q, Wang D H, Sun Y, Zhao Z, Liu S B, Wang C H and Guo W M. 2021. Review on research and exploration of the 3R mineral resources during the past 70 years by Institute of Mineral Resources[J]. Mineral Deposits, 40(4): 655-692(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Z L, Qiu J S, Xing G F, Yu M G and Zhao J L. 2014. Petrogenesis and magmatic evolution of the Yashan granite plution in Yichun, Jiangxi Province, and their constraints on mineralization[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 88(5): 850-868(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yin R, Huang X L, Wang R C, Sun X M, Tang Y, Wang Y and Xu Y G. 2022. Rare-metal enrichment and Nb-Ta fractionation during magmatic-hydrothermal processes in rare-metal granites: Evidence from zoned micas from the Yashan Pluton, South China[J]. Journal of Petrology, 63(10): egac093.
Zhang F S, Xu J, Zhang J and Guo J S. 2020. Geochemical characteristics, zircon U-Pb age and geological significance of New Proterozoic granites in Jiuling area, Jiangxi Province[J]. Journal of East China University of Technology ( Natural Science), 43(1): 12-20(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Y, Pan J Y, Ma D S, Dan X H, Zhang L L, Xu G H, Yang C P, Jiang Q X and Jiang C Q. 2017. Re-Os molybdenite age of Dawutang tungsten ore district of Northwest Jiangxi and its geological significance[J]. Mineral Deposits, 36(3): 749-769(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Y, Pan J Y and Ma D S. 2020. Lithium element enrichment and inspiration for prospecting for rare-metal mineralization in the Dahutang tungsten deposit: Constrains from mineralogy and geochemistry of hydrothermal alteration[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 94(11): 3321-3342(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Z H, Zhang D, He X L, Hu B J, Zhu X Y, Du Z Z, Jia W B and Gong X D. 2021. Biotite granodiorite age of Jiuling complex in Jiangxi Province and its limitation on the collision and splicing time of the Yangtze and Cathay plates[J]. Geology in China, 48(5): 1562-1579(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao J H, Zhou M F and Zheng J P. 2013. Constraints from zircon U-Pb ages, O and Hf isotopic compositions on the origin of Neoproterozoic peraluminous granitoids from the Jiangnan Fold Belt, South China[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 166(5): 1505-1519.
Zhong Y F, Ma C Q, Yu Z B, Lin G C, Xu J H, Wang R J, Yang K G and Liu Q. 2005. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronology of the Jiuling granitic complex batholith in Jiangxi Province[J]. Earth Science, 30(6): 685-691(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhou J T, Wang G B, He S F and Fan A C. 2011. Diagenesis and mine-ralization of ganfang rock in Yifeng, Jiangxi Province[J]. Journal of East China University of Technology (Natural Science), 34(4): 345-358(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhou J T, Li Z M, Long W. 2013.Detailed investigation report of lithium-bearing chinastone ore in Shiziling mining area, Yifeng County, Jiangxi Province[R]. National geological data Museum(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhu Z Y, Wang R C, Marignac C, Cuney M, Mercadier J, Che X D, Charles N and Lespinasse M. 2019. Petrogenesis of Nb-(Ta) aplo-pegmatites and fine-grained granites from the Early Cretaceous Huangshan rare-metal granite suite, Northeast Jiangxi Province, Southeast China[J]. Lithos, 364-347: 105150.
Zuo M L. 2016. The reasearch of differences of the rare-metal granites mineralization between Yichun Yashan and Quannan Dajishan in Jiangxi Province[D]. Supervisor: Zhang D H. Beijing: China University of Geosciences. 26-28(in Chinese with English abstract).
附中文参考文献
段政,廖圣兵,褚平利,黄文成,朱延辉,舒徐洁,李长波. 2019.江南造山带东段新元古代九岭复式岩体锆石U-Pb年代学及构造意义[J].中国地质, 46(3): 493-516.
侯可军,李延河,田有荣. 2009. LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石微区原位U-Pb定年技术[J].矿床地质, 28(4): 481-492.
黄兰椿, 蒋少涌. 2012. 江西大湖塘钨矿床似斑状白云母花岗岩锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学及成因研究[J]. 岩石学报, 28(12): 3887-3900.
黄小龙,王汝成,陈小明,刘昌实. 2001.江西雅山富氟高磷花岗岩中的磷酸盐矿物及其成因意义[J].地质论评, 47(5): 542-550.
姜宝亮, 赵劲, 林梅花, 张磊. 2022. 江西省宜丰县白水洞锂铌钽矿床成矿岩浆岩锆石U-Pb年龄及意义[J]. 世界有色金属, (19): 73-75.
李福春,朱金初,金章东. 2000.华南富锂氟含稀有金属花岗岩的成因分析[J].矿床地质, 19(4): 376-385.
李建康,张德会,王登红,张文淮. 2008.富氟花岗岩浆液态不混溶作用及其成岩成矿效应[J].地质评论, 54(2): 175-183.
李建康,刘喜方,王登红. 2014.中国锂矿成矿规律概要[J].地质学报, 88(12): 2269-2283.
李建康,李鹏,陈振宇. 2023.锂铍等战略性金属矿产资源成矿规律与预测评价:前言[J].岩石学报, 39(7): 1881-1886.
李洁,黄小龙. 2013.江西雅山花岗岩岩浆演化及其Ta-Nb富集机制[J].岩石学报, 29(12): 4311-4322.
李洁. 2015.华南中生代稀有金属花岗岩岩浆演化与热液作用过程的矿物学约束[D].导师:黄小龙.广州:广州地球化学研究所. 89-95.
李胜虎. 2015.华南典型花岗岩型稀有金属矿床的成矿机制与找矿模式研究[D].导师:张德会,李健康.北京:中国地质大学. 111-117.
刘涛. 2023.赣东北灵山岩体岩浆-热液演化与铌钽成矿机制研究[D].导师:蒋少涌.北京:中国地质大学. 43-44.
刘泽,陈振宇,王成辉. 2023.赣西北狮子岭花岗岩型锂-钽矿床的矿物学特征及成矿机制[J].岩石学报, 39(7): 2045-2062.
楼法生, 沈渭洲, 王德滋, 舒良树, 吴富江, 张芳荣, 于津海. 2005. 江西武功山穹隆复式花岗岩的锆石U-Pb年代学研究[J]. 地质学报, 79(5): 636-644.
聂晓亮,王水龙,刘爽,徐林. 2022.江西茜坑锂矿床地质地球化学特征与锂云母40Ar/39Ar年代学研究[J].矿物学报, 42(3): 285-294.
潘大鹏,王迪,王孝磊. 2017.赣西北大湖塘石门寺钨矿区花岗岩的成因及其对钨矿的指示意义[J].中国地质, 44(1): 118-135.
秦程. 2018.江西宜丰狮子岭白云母花岗岩成矿潜力研究[D].导师:刘学飞.北京:中国地质大学. 23-42.
孙克克,陈斌,陈军胜,项新葵. 2017.江西大湖塘矿区九岭花岗闪长岩的成因及其构造意义[J].岩石学报, 33(3): 907-924.
孙艳,王成辉,郭唯明,王登红,杨岳清,凡秀军,陈莉. 2018.赣西北狮子岭花岗岩中锂、铷、铯的赋存状态及应用前景[A].第十四届全国矿床会议论文集[C]. 376-377.
王成辉,杨岳清,王登红,孙艳,陈振宇,谢国刚,凡秀军. 2018.江西九岭地区三稀调查发现磷锂铝石等锂铍锡钽矿物[J].岩矿测试, 37(1): 108-110.
王成辉,王登红,陈晨,刘善宝,陈振宇,孙艳,赵晨辉,曹圣华,凡秀军. 2019.九岭式狮子岭岩体型稀有金属成矿作用研究进展及其找矿意义[J].地质学报, 93(6): 1359-1373.
王成辉,王登红,刘善宝,许建祥,秦锦华,秦燕,刘金宇,赵正,冯文杰,刘战庆,赵如意,郭春丽. 2022.赣南石雷钨锡矿云英岩型锂矿找矿新发现及其区域成矿潜力分析[J].中国地质, 49(6): 1834-1844.
王登红,刘善宝,于扬,王成辉,孙艳,代鸿章,李建康,代晶晶,王裕先,赵汀,马圣钞,刘丽军. 2019.川西大型战略性新兴产业矿产基地勘查进展及其开发利用研究[J].地质学报, 93(6): 1444-1453.
吴福元,郭春丽,胡方泱,刘小驰,赵俊兴,李晓峰,秦克章. 2023.南岭高分异花岗岩成岩与成矿[J].岩石学报, 39(1): 1-36.
吴学敏,周敏娟,罗喜成,周建廷. 2016.江西西北部锂及稀有金属成矿条件及找矿潜力分析[J].华东地质, 37(4): 275-283.
杨岳清,王登红,孙艳,赵芝,刘善宝,王成辉,郭维明. 2021.矿产资源研究所“三稀”矿产研究与找矿实践70年历程——回顾与启示[J].矿床地质, 40(4): 655-692.
杨泽黎,邱检生,邢光福,余明刚,赵姣龙. 2014.江西宜春雅山花岗岩体的成因与演化及其对成矿的制约[J].地质学报, 88(5): 850-868.
张福神,徐进,张娟,郭金山. 2020.江西九岭地区新元古代花岗岩地球化学特征、锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J].东华理工大学学报(自然科学版), 43(1): 12-20.
张勇,潘家永,马东升,但小华,张雷雷,徐国辉,杨春鹏,江青霞,江超强. 2017.赣西北大雾塘钨矿区地质特征及Re-Os同位素年代学研究[J].矿床地质, 36(3): 749-769.
张勇,潘家永,马东升. 2020.赣西北大湖塘钨矿富锂-云母化岩锂元素富集机制及其对锂等稀有金属找矿的启示[J].地质学报, 94(11): 3321-3342.
张志辉,张达,贺晓龙,胡擘捷,祝新友,杜泽忠,贾文彬,巩小栋. 2021.江西九岭杂岩体中黑云母花岗闪长岩年龄及对扬子和华夏板块碰撞拼合时间限定[J].中国地质, 48(5): 1562-1579.
钟玉芳,马昌前,佘振兵,林广春,续金海,王人镜,杨坤光,刘强. 2005.江西九岭花岗岩类复式岩基锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年代学[J].地球科学, 30(6): 685-691.
周建廷,王国斌,何淑芳,范爱春. 2011.江西宜丰地区甘坊岩体成岩成矿作用分析[J].东华理工大学学报(自然科学版), 34(4): 345-358.
周建廷,李自敏,龙悟. 2013.江西省宜丰县狮子岭矿区含锂瓷石矿详查报告[R].全国地质资料馆.
左梦璐. 2016. 江西雅山与大吉山两类稀有金属花岗岩成矿差异性研究[D]. 导师: 张德会. 北京: 中国地质大学. 26-28.
摘要
赣西北矿集区是中国重要的花岗岩型锂矿资源基地,以发育多期次多阶段岩浆作用和大规模锂等稀有金属矿床著称。区内花岗质岩浆与稀有金属成矿关系密切,为进一步研究该地区花岗质岩浆演化特征及其与稀有金属成矿的联系,确定相关花岗岩成岩时代及成因类型,查明稀有金属成矿机制,笔者选择九岭地区狮子岭花岗岩作为研究对象,对其开展了岩相学、锆石U-Pb年代学及岩石地球化学分析。结果显示,狮子岭花岗岩属高钾钙碱性系列,具有高Si,富P,贫Ca、Mg、Fe,富集U、Hf等高场强元素,亏损Ba、Sr等大离子亲石元素,稀土元素总量较低(ΣREE=2.12×10-6~146.24×10-6),轻稀土元素相对富集(LREE/HREE=3.5~16.53),弱Eu负异常(δEu=0.23~0.59)的特征。整体上具有S型花岗岩的地球化学特征。锆石U-Pb定年显示,黑云母二长花岗岩成岩年龄为(141.02±0.59)Ma,锂(白)云母碱长花岗岩成岩年龄为(113.96±0.72)Ma。锂(白)云母碱长花岗岩成岩过程中形成磷锂铝石及锂云母等含锂矿物,其成岩年龄可视为锂等稀有金属成矿年龄。该区稀有金属矿化受燕山晚期岩浆结晶分异作用及后期热液交代作用共同影响,岩浆结晶分异作用是Li、Nb、Ta成矿的决定性因素,后期热液交代作用为Li等成矿元素的二次富集提供条件。
Abstract
The ore cluster in northwestern Jiangxi Province is a significant granite-type lithium mineral resource base which is characterized by multi-stage magmatism and large-scale mineralization of rare metals like lithium. The granitic magma and rare-metal mineralization are intimately connected, then we further study the evolution characteristics of granitic magma in this area and its relationship with rare metal mineralization, define the petrogenic age and genetic types of related granites, and find out the mechanism of rare metal mineralization. In this study, the Shiziling granites in Jiuling area were selected as the research object, petrography, zircon U-Pb geochronology and petrogeochemistry analysis of the granites were carried out. Results show that the Shiziling gra-nites are high-K calc-alkaline series, and rich in Si and P, deplete in Ca, Mg, and Fe. Moreover, these rocks enrich in the high field strength elements (HFSE, e.g., U, Hf), and deplete in the large-ion lithophile elements (LILE, e.g., Ba, Sr). The rocks have lower total rare earth elements (REE), range from 2.12×10-6to 146.24×10-6. The ratio of LREE/HREE is relatively high (3.5~16.53). The rocks show weak negative Eu anomalies (δEu=0.23~0.59). Overall, the Shiziling granites have geochemical characteristics of S-type granite. The zircon U-Pb dating results show that the petrogenic age of biotite monzogranite is (141.02±0.59) Ma, and the lepidolite(muscovite) alkali feldspar granite is (113.96±0.72) Ma. Amblygonite and lepidolite minerals formed in the petrogenic process of lepidolite(muscovite) alkali feldspar granite, so the petrogenic age of alkali feldspar granite could be regarded as the metallogenetic age of rare metals. Rare metal mineralization was influenced by the Early stage of Yanshanian magmatic crystallization differentiation and the late hydrothermal metasomatism, magmatic crystallization differentiation is the determinants for the mineralization of Li, Nb, and Ta mineralization, hydrothermal alteration in the late stage provides the conditions for the secondary enrichment of Li.