пјҲ1 дёӯеӣҪең°иҙЁз§‘еӯҰйҷўзҹҝдә§иө„жәҗз ”з©¶жүҖ еӣҪеңҹиө„жәҗйғЁжҲҗзҹҝдҪңз”ЁдёҺиө„жәҗиҜ„д»·йҮҚзӮ№е®һйӘҢе®ӨпјҢ еҢ—дә¬ 100037пјӣ 2 дёӯеӣҪең°иҙЁеӨ§еӯҰпјҢ еҢ—дә¬100083пјӣ 3 еӣҪ家ең°иҙЁе®һйӘҢжөӢиҜ•дёӯеҝғпјҢ еҢ—дә¬1000 37пјү
第дёҖдҪңиҖ…з®Җд»Ӣеӯҷе°Ҹиҷ№пјҢ еҘіпјҢ 1983е№ҙз”ҹпјҢ еҚҡеЈ«еҗҺпјҢ й«ҳзә§е·ҘзЁӢеёҲпјҢ зҹҝдә§жҷ®жҹҘдёҺеӢҳжҺўдё“дёҡ гҖӮ Emaiпјҡ sxhbei@163.com **йҖҡи®ҜдҪңиҖ…еҲҳжҲҗжһ—пјҢ з”·пјҢ 1963е№ҙз”ҹпјҢ з ”з©¶е‘ҳпјҢ еҚҡеЈ«з ”з©¶з”ҹеҜјеёҲпјҢ дё»иҰҒд»ҺдәӢй’ҫзӣҗзӯүжІү з§ҜдёҺйқһйҮ‘еұһзҹҝз ”з©¶гҖӮ Emailпјҡ liuchengl@263.net
收зЁҝж—Ҙжңҹ2016-08-30;
ж”№еӣһж—Ҙжңҹ2016-10-10
жң¬ж–Үеҫ—еҲ°дёӯеӣҪең°иҙЁз§‘еӯҰйҷўеҹәжң¬з§‘з ”дёҡеҠЎиҙ№йЎ№зӣ®пјҲзј–еҸ·пјҡ K1405пјүгҖҒеӣҪ家йҮҚзӮ№еҹәзЎҖз ”з©¶и®ЎеҲ’вҖң 973
В В В В p oint of potash minerals during Triassic: Evidence from chemicalВ
В В В В compos ition of fluid inclusions in haliteВ
(1 MLR Key Laboratory of Metallogeny and Mineral Assessment, Institute of Minera l Resources, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Beiji ng 100037, China; 2 China University of Geosciences, Beijing 100083, China; 3 National Research Center for Geoanalysis, Beijing 100037, China)
|
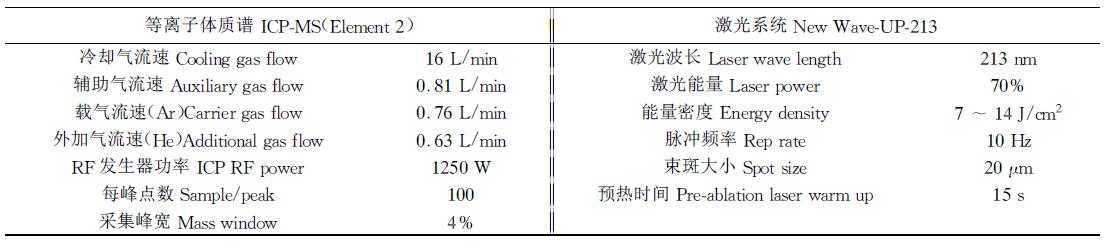
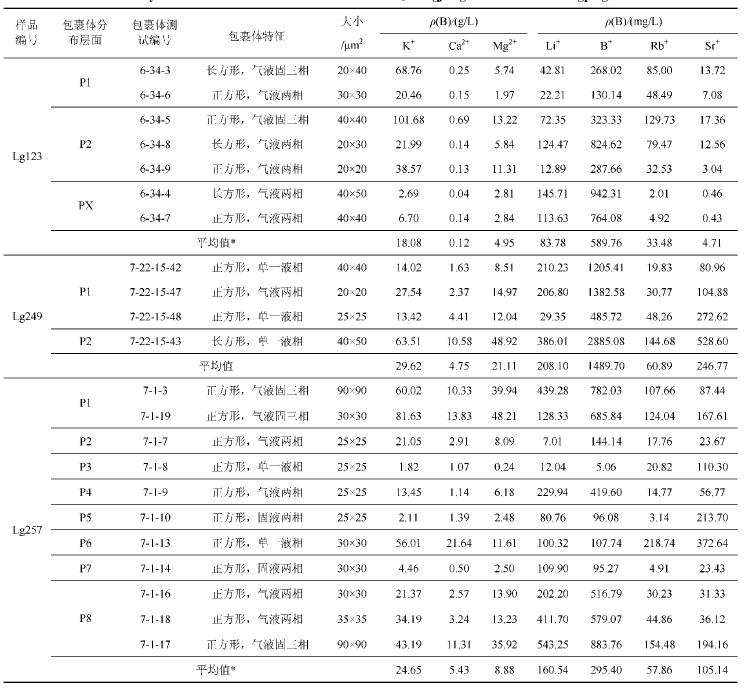
иЎЁ 1LA_ICP_MSе·ҘдҪңеҸӮж•°
Table 1Laser ablation (LA)_ICP_MS operating conditions
|
|
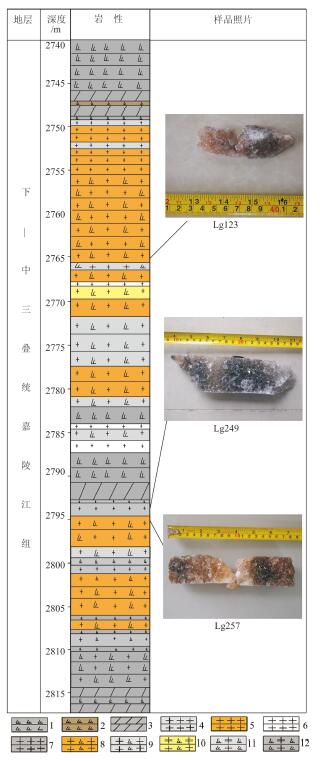
еӣҫ 1й•ҝе№і3дә•еҳүйҷөжұҹеӣӣж®өеІ©еҝғжҹұзҠ¶з®ҖеӣҫеҸҠж ·е“ҒеІ©иҠҜз…§зүҮ
1вҖ”ж·ұзҒ°иүІзЎ¬зҹіиҶҸпјӣ 2вҖ”иӨҗиүІзЎ¬зҹіиҶҸпјӣ 3вҖ”ж·ұзҒ°иүІзҷҪдә‘еІ©пјӣ 4вҖ”зҒ°иүІзҹізӣҗпјӣ 5вҖ”ж©ҳиүІзҹізӣҗпјӣ 6вҖ”зҷҪиүІзҹізӣҗпјӣ 7вҖ”ж·ұзҒ°иүІзҹізӣҗпјӣ 8вҖ”ж©ҳиүІеҗ«зЎ¬зҹіиҶҸзҹі
зӣҗеІ©пјӣ 9вҖ”зҒ°иүІеҗ«зЎ¬зҹіиҶҸзҹі зӣҗеІ©пјӣ 10вҖ”й»„иүІеҗ«зЎ¬зҹіиҶҸзҹізӣҗеІ©пјӣ 11вҖ”зҒ°иүІеҗ«зҹізӣҗзЎ¬зҹіиҶҸпјӣ 12вҖ”ж·ұзҒ°иүІеҗ«зҹізӣҗзЎ¬зҹіиҶҸ
Fig. 1Core histogram and halite in the forth member of Jialingjiang Formation of Changping third well
1вҖ”Dark gray anhydrite; 2вҖ”Brown anhydrite; 3вҖ”Dark gray dolomite; 4вҖ”Gray halit e; 5вҖ”Orange haliteпјӣ 6вҖ”White haliteпјӣ 7вҖ”Dark gray haliteпјӣ 8вҖ”Orange anhydrit e-bearing halite; 9вҖ”Gray anhydrite-bearing halite; 10вҖ”Yellow anhydrite_beari ng halite; 11вҖ”Gray salt-bearing anhydriteпјӣ12вҖ”Dark gray salt_bearing anhydrite
|
|
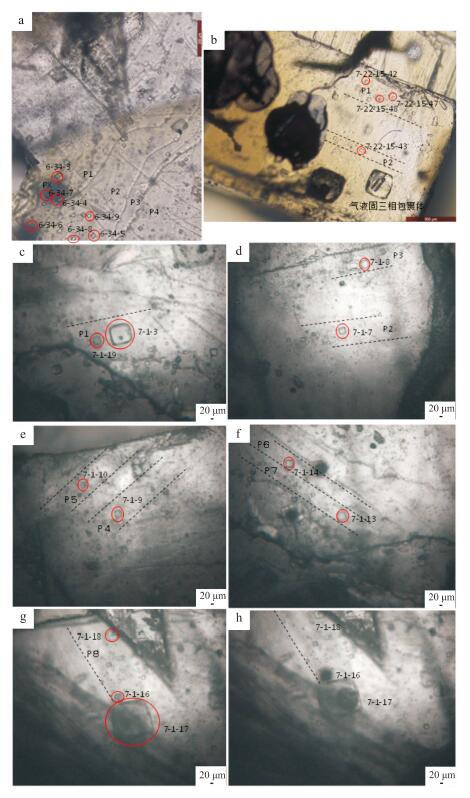
еӣҫ 2зҹізӣҗжөҒдҪ“еҢ…иЈ№дҪ“жҳҫеҫ®й•ңз…§зүҮ
a. ж ·е“ҒLg123пјӣ b. ж ·е“ҒLg249пјӣ cпҪһh. ж ·е“ҒLg257; g. еҢ…иЈ№дҪ“7_1_16иў«жҝҖе…үеүҘиҡҖеүҚзҡ„з…§зүҮ ; h. еҢ…иЈ№дҪ“7_1_16иў«жҝҖе…үеүҘиҡҖ
еҗҺзҡ„з…§зүҮ. 6_34_3гҖҒ6_34_4зӯүдёәеҢ…иЈ№дҪ“жөӢиҜ•зј–еҸ·пјӣ P1пҪһPXиЎЁзӨәеҢ…иЈ№дҪ“жүҖеӨ„жҷ¶йқў
Fig. 2Fluid inclusions in halite
a. Sample Lg123; b. Sample Lg249; cпҪһh. Sample Lg257; g. Photo of fluid inclusio n (7_1_16) before laser ablation; h. Photo of fluid
inclusion (7_1_16) after l as er ablation. 6_34_3, 6_34_4 et al: Analysis number for inclusions; P1пҪһPX: Faces that inclusions are in
|
|
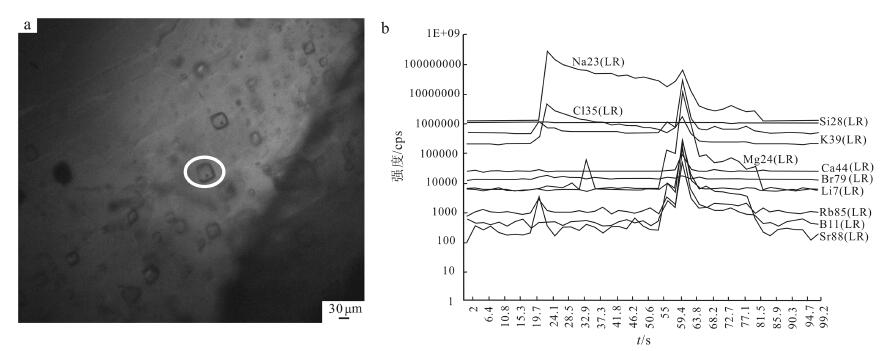
еӣҫ 3зҹізӣҗжөҒдҪ“еҢ…иЈ№дҪ“пјҲaпјүе’ҢзҹізӣҗеҚ•дёӘеҢ…иЈ№дҪ“иҙЁи°ұдҝЎеҸ·ејәеәҰйҡҸж—¶й—ҙзҡ„еҸҳеҢ–пјҲbпјү
Fig. 3The fluid inclusion in halite (a) and MS signal intensity vs. time for s ingle fluid inclusion in halite (b)
|
|
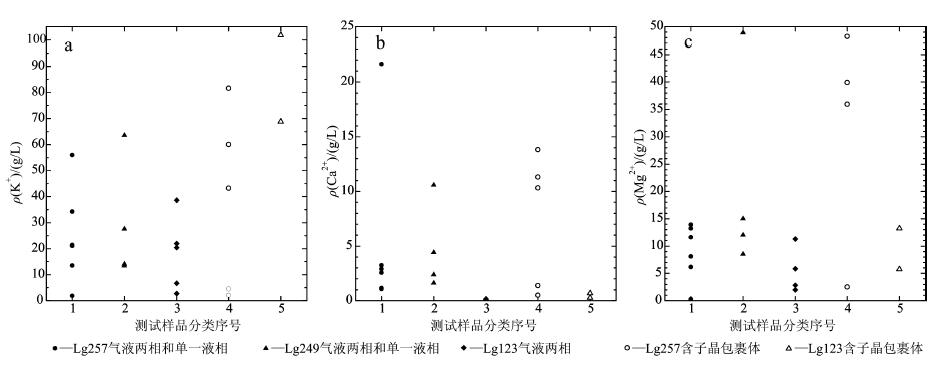
еӣҫ 4зҹізӣҗжөҒдҪ“еҢ…иЈ№дҪ“дёӯKпјҲеӣҫaпјүгҖҒCaпјҲеӣҫbпјүгҖҒMgпјҲеӣҫcпјүдёүз§Қе…ғзҙ зҡ„еҗ«йҮҸ
Fig. 4Content of potassium (a), calcium (b) and magnesium (c) in fluid inclusi ons in halites
|
|
иЎЁ 2й•ҝе№і3дә•еҳүйҷөжұҹз»„зҹізӣҗжөҒдҪ“еҢ…иЈ№дҪ“жҲҗеҲҶеҲҶжһҗз»“жһң
Table 2 Analytical results of fluid inclusions in halites in Jialingjiang Format ion of Changping third well
|
еҲҶжһҗз»“жһңиҝҳжҳҫзӨәпјҢеҗҢдёҖж ·е“Ғзҡ„дёҚеҗҢжөҒдҪ“еҢ…иЈ№дҪ“ еҢ–еӯҰз»„еҲҶеҸҳеҢ–иҫғеӨ§пјҲеӣҫ4гҖҒиЎЁ2пјүпјҢж №жҚ®еҢ…иЈ№дҪ“еІ©зӣёеӯҰ и§ӮеҜҹеҸҜзҹҘпјҢжүҖжөӢиҜ•еҢ…иЈ№дҪ“еӨ„дәҺдёҚеҗҢзҡ„зҹізӣҗжҷ¶дҪ“йқўP1пҪһPXпјҲеӣҫ2пјүгҖӮж ·е“ҒLg123еҢ…иЈ№дҪ“дёӯ ПҒ (K+)дёә2.69пҪһ38.57 g/LпјҲеү”йҷӨеҗ«еӯҗжҷ¶еҢ…иЈ№дҪ“зҡ„ж•°жҚ®пјҢдёӢеҗҢпјүпјҢеҢ…иЈ№дҪ“еҲҶеёғдәҺ3дёӘ жҷ¶йқўдёҠпјҢе…¶дёӯP2жҷ¶йқўдёҠ2дёӘж°”ж¶ІдёӨзӣёеҢ…иЈ№дҪ“пјҲ6_34_8е’Ң6_34_9пјүзҡ„ПҒ(K+)гҖҒ ПҒ(Mg2+)зӯүжҺҘиҝ‘пјҢPXжҷ¶йқўдёҠ2дёӘжөҒдҪ“еҢ…иЈ№дҪ“еҢ–еӯҰз»„жҲҗеҲҶжҜ”иҫғжҺҘиҝ‘гҖӮLg249еҢ…иЈ№ дҪ“ дёӯПҒ(K+)дёә13.42пҪһ63.51 g/LпјҢLg257еҢ…иЈ№дҪ“дёӯПҒ(K+)дёә1.82 пҪһ56.01 g/LпјҢеӨ„дәҺеҗҢдёҖжҷ¶йқўдёҠзҡ„еҢ…иЈ№дҪ“еҢ–еӯҰз»„еҲҶеҸҳеҢ–иҫғе°ҸпјҢиҖҢдёҚеҗҢжҷ¶йқўдёҠеҢ…иЈ№дҪ“з»„еҲҶеҸҳеҢ– иҫғеӨ§гҖӮ
|
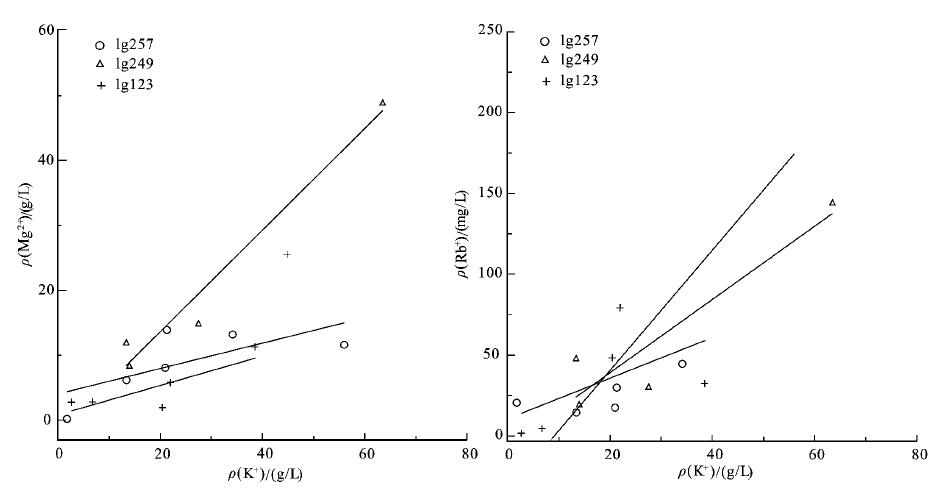
еӣҫ 5зҹізӣҗжөҒдҪ“еҢ…иЈ№дҪ“й’ҫеҗ«йҮҸдёҺй•ҒгҖҒй“·еҗ«йҮҸзҡ„е…ізі»
Fig. 5Relationship between content of potassium and that of magnesium, between content of potassium and that of
rubidium in fluid inclusions in halites
|
|
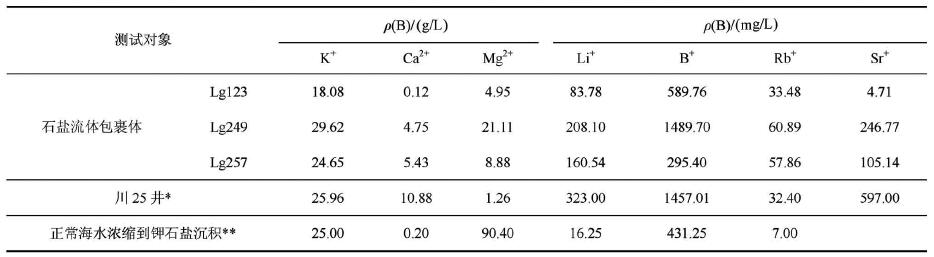
иЎЁ 3зҹізӣҗжөҒдҪ“еҢ…иЈ№дҪ“жҲҗеҲҶдёҺе·қ25дә•гҖҒй»„жө·жө·ж°ҙжө“зј©еҲ°й’ҫзҹізӣҗжІүз§Ҝж—¶жңҹеҚӨж°ҙжҲҗеҲҶеҜ№жҜ”
Table 3Chemical composition of fluid inclusions in halite in Sichuan Basin, br ine in Chuang 25# hole,
and Yellow Sea water after sylvite deposition in the evaporation process
|
еҸҰеӨ–пјҢеңЁе·қдёңеҢ—е·қ25 дә•й’»йҒҮзҡ„еҜҢй’ҫеҚӨж°ҙпјҢдёҖиҲ¬ и®ӨдёәпјҢжҳҜжІүз§ҜеҸҳиҙЁе’ҢеӣәжҖҒй’ҫзӣҗжә¶ж»Өзҡ„еӨҚеҗҲжҲҗеӣ пјҲжһ—иҖҖеәӯпјҢ1995пјӣжһ—иҖҖеәӯзӯүпјҢ2002aпјӣ2002bпјӣ жқҺ дәҡж–ҮзӯүпјҢ1998пјүпјҢиҖҢзҹізӣҗеҢ…иЈ№дҪ“жөҒдҪ“е№іеқҮз»„жҲҗдёҺе·қ25дә• еҚӨж°ҙз»„жҲҗеҹәжң¬дёҖиҮҙпјҲиЎЁ3пјүпјҢеҸҜд»ҘиҜҙжҳҺе·қ25дә•еҚӨж°ҙеә”дёәеҺҹз”ҹжІүз§ҜеҚӨж°ҙпјҢ并йқһж·Ӣж»Ө жҲҗеӣ гҖӮиҝҷдёҺзӣҶең°еҸӨжө·ж°ҙеңЁжІүз§Ҝд»ҘеҗҺеҹәжң¬еӨ„дәҺж·ұеҹӢе°Ғй—ӯзҺҜеўғпјҢдёҚе…·еӨҮжё—е…Ҙж°ҙж·Ӣж»ӨжқЎд»¶зҡ„и§ӮзӮ№пјҲ е®Ӣй№ӨеҪ¬зӯүпјҢ1988пјүжҳҜзӣёеҗ»еҗҲзҡ„гҖӮ
дёҖиҲ¬и®ӨдёәеңЁеҚӨж°ҙи’ёеҸ‘жө“зј©иҝҮзЁӢдёӯпјҢж—©жңҹжһҗеҮәзҹіиҶҸпјҢйҡҸзқҖй’ҫгҖҒй•Ғеҗ«йҮҸзҡ„еҚҮй«ҳпјҢеңЁжҢҒз»ӯи’ёеҸ‘жө“зј© зҡ„жқЎд»¶дёӢпјҢе°ҶеҪўжҲҗй’ҫзӣҗгҖӮжқӮеҚӨзҹіжҳҜжңҖжҳ“дҝқеӯҳзҡ„й’ҫзӣҗзҹҝзү©д№ӢдёҖпјҢж— и®әе…¶жҲҗеӣ еҰӮдҪ•пјҢжқӮеҚӨзҹізҡ„еӯҳ еңЁ йғҪеҸҜд»ҘиҜҙжҳҺзӣҶең°дёӯеҸҜиғҪеӯҳеңЁжҳ“жә¶й’ҫзӣҗзҹҝзү©жҲ–зҹҝеұӮгҖӮеҢ…иЈ№дҪ“еҲҶжһҗз»“жһңиҝҳжҳҫзӨәпјҢеҗ«еӯҗжҷ¶зҡ„зҹізӣҗжөҒ дҪ“еҢ…иЈ№дҪ“дёӯй’ҫеҗ«йҮҸПҒ(K+)жҳҺжҳҫй«ҳдәҺж°”ж¶ІдёӨзӣёе’ҢеҚ•дёҖж¶ІзӣёдёӨзұ»еҢ…иЈ№дҪ“дёӯй’ҫеҗ«йҮҸпјҢиҖҢПҒ (Mg2+)е’ҢПҒ(Ca2+)еҹәжң¬дёҖиҮҙпјҲеӣҫ4пјүпјҢеӣ иҖҢжҺЁжөӢзҹізӣҗеҢ…иЈ№дҪ“дёӯзҡ„ еӯҗжҷ¶еҫҲеҸҜиғҪжҳҜй’ҫзҹізӣҗзҹҝзү©гҖӮжӯӨеӨ–пјҢйҖҡиҝҮжү«жҸҸз”өй•ң иғҪи°ұеҲҶжһҗз–‘дјји§Ғеҫ®йҮҸй’ҫзҹізӣҗпјҲиөөиүіеҶӣзӯүпјҢ2015пјүпјҢиҝӣдёҖжӯҘиҜҙжҳҺе·қдёңең°еҢәеұҖйғЁеҸӨзӣҗж№–еҸҜиғҪжңүй’ҫ зҹізӣҗжһҗеҮәгҖӮ
пјҲ1пјү зҹізӣҗж ·е“ҒеҢ…иЈ№дҪ“еҢ–еӯҰз»„жҲҗз»“жһңиЎЁжҳҺеӣӣе·қзӣҶең°дёүеҸ зәӘеҸӨжө·ж°ҙеҜҢMgиҙ«CaпјҢдёәMg_SO4еһӢжө· ж°ҙгҖӮ
пјҲ2пјү зҹізӣҗжөҒдҪ“еҢ…иЈ№дҪ“дёӯПҒ(K+)е№іеқҮдёә24.12 g/LпјҢдёҺзҺ°д»Јжө·ж°ҙжө“зј©еҲ°й’ҫ зҹі зӣҗжһҗеҮәйҳ¶ж®өзҡ„ПҒ(K+)еҹәжң¬дёҖиҮҙпјҢжҺЁж–ӯдёүеҸ зәӘеӣӣе·қзӣҶең°еҸӨжө·ж°ҙеҸҜиғҪе·ІиҫҫеҲ°й’ҫзҹізӣҗжһҗ еҮәйҳ¶ж®өгҖӮ
еҝ—и°ўеӣӣе·қзӣҶең°й’»дә•ж ·е“ҒйҮҮйӣҶиҝҮзЁӢеҫ—еҲ°дёӯзӣҗйҮҚеәҶй•ҝеҜҝзӣҗеҢ–жңүйҷҗе…¬еҸёйўҶеҜјеҸҠдёӯеӣҪ ең°иҙЁз§‘еӯҰйҷўжҲҗйғҪзҹҝдә§з»јеҗҲеҲ©з”Ёз ”究жүҖйҫҡеӨ§е…ҙеҚҡеЈ«зӯүеҚҸеҠ©пјҢеңЁжӯӨиЎЁзӨәж„ҹи°ўгҖӮ
В В В В Khmelevska V M, Peryt T M and Petrichenko O I. 1998. Secular variation in seawat er chemistry during the Phanerozoic as indicated by brine inclusions in haliteпј» JпјҪ. The Journal of GeologyпјҢ106: 695_712.
В В В В Cai K Q and Yuan J Q. 1986. Metallogenic conditions and prospecting direction fo r the Triassic potash deposits in Sichuan Basinпј»JпјҪ. Geology of Chemical Mi nerals, 8(2):4_12 (in Chinese).
В В В В Chen Y H. 1983. Sequence of salt separation and regularity of some trace element s distribution during isothermal evaporation(25в„ғ) of the Huanghai sea waterпј»J пјҪ. Acta Geologica Sinica, (4): 379_390 (in Chinese with English abstract)пјҺ
В В В В Frezzotti M L, Tecce F and Casagli A. 2011. Raman spectroscopy for fluid inclusi on analysisпј»JпјҪ. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 112: 1_20.
В В В В Ghazi A M and Stephen S. 2000. Trace element determination of single fluid inclu sions by laser ablation ICP_MS: Applications for halites from sedimentary basins пј»JпјҪ. The Analyst, 125 (1): 205_210.
В В В В Hardie L A, Lowenstein T K and Spencer R J. 1985. The problem of distinguishing between primary and secondary features in evaporatesпј»AпјҪ. In: Schreiber B C , Harb er H I, eds. Sixth International Symposium on Saltпј»CпјҪ. Alexandia, Virginia, US A: The Salt Institute, 11_39.
В В В В Hardie L A.1996. Secular variation in seawater chemistry: An explanation for the coupled secular variation in the mineralogies of marine limestones and potash e vaporites over the past 600 m.yпј»JпјҪ. Geology, 24: 279_283.
В В В В Hu M Y, He H L, Zhan X C, Fan X T, Wang G and Jia Z R. 2008. Matrix normalizatio n for in_situ multi_element quantitative analysis of zircon in Laser Ablation_In ductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometryпј»JпјҪ. Chinese Journal of Analytic al Chemistry, 36(7): 947_953 (in Chinese with English abstract).
В В В В Hu S H, Hu Z C, Liu Y S, Luo Y, Lin S L and Gao S. 2001. New techniques of major and minor elemental analysis in individual fluid inclusion_laser ablation induc tively coupled plasma mass spectrometry(LA_ICP_MS)пј»JпјҪ. Earth Science Frontiers , 8(4): 434_440 (in Chinese with English abstract).
В В В В Huang J G. 1998. The Triassic potash deposits in China: An example from the Sich uan Basinпј»JпјҪ. Sedimentary Facies and Palaeogeography, 18(4):23_43 (in Chinese with English abstract).
В В В В Khmelevska V M, Peryt T M, Zang W and Vovnyuk S V. 2006. Composition of brines i n halite_hosted fluid inclusions in the upper Ordovician, Canning Basin, western Australia: New data on seawater chemistryпј»JпјҪ. Terra Nova, 18(2): 95_103.
В В В В Kovalevych V M, Marshall T, Peryt T M, Petrychenko O Y and Zhukova S A. 2006. Ch emical composition of seawater in Neoproterozoic: Results of fluid inclusion stu dy of halite from Salt Range (Pakistan) and Amadeus Basin (Australia)пј»JпјҪ. Prec ambrian Research, 144: 39_51.
В В В В Li Y W, Cai K Q and Han W T. 1998. Origin of potassium_rich brine and the metamo rphism of Triassic evaporites in Sichuan Basinпј»JпјҪ. Geoscience, 12(2): 222_228 (in Chinese with English abstract).
В В В В Lin Y T. 1994. On K_bearing property of the marine Triassic and search for potas h salt in Sichuan Basinпј»JпјҪ. Acta Geologica Sichuan, 14(2):111_120(in Chinese w ith English abstract).
В В В В Lin Y T. 1995. Metamorphism of Triassic salt depositions in Sichuan Basin and it s guide to prospecting for potash resourcesпј»JпјҪ. Geology of Chemical Minerals, 17(2):93_102 (in Chinese with English abstract)
В В В В Lin Y T and Xu Z L. 2009. Significance of salts preservation condition research on finding potassium of the Triassic in Sichuan Basinпј»JпјҪ. Journal of Salt Lake Research, 17(1):6_12(in Chinese with English abstract).
В В В В Lin Y T, He J Q, Wang T D and Ye M C. 2002a. Geochemical characteristics of pota s sium_rich brine in middle Triassic Chendu Salt Basin of Sichuan Basin and its pr ospects for brine tappingпј»JпјҪ. Geology of Chemical Minerals, 24пјҲ2пјүпјҡ72_84 (in Chinese with English abstract)
В В В В Lin Y T and Zhen M Q. 2002b. Theory on guidance of heat_melted salt of Triassic p eriod in search of potash in Sichuan Basinпј»JпјҪ. Journal of Salt Lake Research, 10(1): 8_17 (in Chinese with English abstract).
В В В В Liu X Q, Ni P, Dong H L and Wang T G. 2007. Homogenization temperature and its s ignificance for primary fluid inclusion in halite formed in Chaka salt lake, Qar dam basinпј»JпјҪ. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(1): 113_116(in Chinese with English abstract).
В В В В Lu S N, Li H K, Chen Z H, Yu H F, Jin W and Guo K Y. 2004. Relationship between Neoproterozoic Cratons of China and the Rodiniaпј»JпјҪ. Earth Science Frontier s, 11(2): 515_523(in Chinese with English abstract).
В В В В Longerich H P, Jackson S E and Gunther D. 1996. Inter_laboratory note. Laser abl ation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometric transient signal data acquis ition and analyte concentration calculationпј»JпјҪ. Journal of Analytical Atom ic Spectrometry, 11(9): 899_904.
В В В В Lowenstein T K and Hardie L A. 1985. Criteria for the recognition of salt_pan e vaporatesпј»JпјҪ. Sedimentology, 32: 627_644.
В В В В Lowenstein T K and Brennan S T. 2002. Fluid inclusions in paleolimnological stud ies of chemical sediments tracking environmental change using lake sedimentsпј»J пјҪ. In: Last W M and Smol J P, eds. Developments in Paleoenvironmental Research: Sp ringer Netherlands, 189_216.
В В В В Lowenstein T K, Timofeeff M N, Brennan S T, Hardie L A and Demicco R V. 2001 . Os cillations in Phanerozoic seawater chemistry: Evidence from fluid inclusions пј»JпјҪ. Science, 294: 1086_1088.
В В В В Lowenstein T K, Hardie L A, Timofeeff M N and Demicco R V. 2003. Secular variati on in seawater chemistry and the origin of calcium chloride basinal brinesпј»JпјҪ. Geology, 31:857_860.
В В В В Meng F W, Liu C L and Ni P. 2012. To forecast sylvite deposits using the chemist ry of fluid inclusions in haliteпј»JпјҪ. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica, 29(1): 62_69 (in Chinese with English abstract).
В В В В Petrychenko O Y, Peryt T M and Chechel E I. 2005. Early Cambrian seawater chemis try from fluid inclusions in halite from Siberian evaporitesпј»JпјҪ. Chemical Geology, 219: 149_161.
В В В В Qiu Y M, Gao S, McNaughton N J, Groves D I and Ling W. 2000. First evidence of > 3.2 Ga continental crust in the Yangtze craton of South China and its implicatio ns for Archean crustal evolution and Phanerozoic tectonicsпј»JпјҪ. Geology, 28(1): 11_14.В
В В В В Satterfield C L.2005. Paleobrine temperatures, chemistries, and paleoenvironment s of Silurian salina formation F_1 salt, Michigan Basin, USA, from petrography f luid inclusions in haliteпј»JпјҪ. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 75(4): 534_ 546.
В В В В Shepherd T J, Ayora C, Cendon D I, Chenery S R and Moissette A. 1998. Quantitati ve solute ananlysis of single fluid inclusions in halite by LA_ICP_MS and cryo_S EM_EDS: Complementary microbeam techniquesпј»JпјҪ. European Journal of Mineralogy, 10: 1097_1108.
В В В В Shepherd T J and Chenery S R. 1995. Laser ablation ICP_MS elemental ananlysis of individual fluid inclusions: An evaluation studyпј»JпјҪ. Geochimica et Coshmochim ica Acta, 59: 3997_4007.
В В В В Shepherd T J, Naden J, Chenery S R, Milodowski A E and Gillespie M R. 2000. Chem ical analysis of palaeogroundwaters: A new frontier for fluid inclusion research пј»JпјҪ. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 69: 415_418.
В В В В Song H B, Song Z P and Xiao Z Q. 1988. Stable isotope geochemistry of potash_ric h b rine in No.25 well of Xuanhan area in northeastern Sichuan and its potash_prospe cting applicationпј»JпјҪ. Bulletin of the Institute of Mineral Deposits Chinese Ac ademy of Geological Sciences, 1: 51_67 (in Chinese with English abstract).
В В В В Sun X H, Hu M Y, Liu C L, Jiao P C, Ma L C, Wang X and Zhan X C. 2013. Compositi on determination of single fluid inclusions in salt minerals by Laser Ablation ICP_MSпј»JпјҪ. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 41(2), 235_241.
В В В В Timofeeff M N, Blackburn W H and Lowenstein T K. 2000. ESEM_EDS: An improved tec hnique for major element chemical analysis of fluid inclusionsпј»JпјҪ. Chemical Ge ology, 164(3пҪһ4): 171_182.
В В В В Timofeeff M N, Lowenstein T K, Brennan S T, Demicco R V, Zimmermann H, Horita J and von Borstel L E. 2001. Evaluating seawater chemistry from fluid inclusions i n halite: Examples from modern marine and nonmarine environmentsпј»JпјҪ. Geochimic a et Cosmochimica Acta, 65 (14): 2293_2300.
В В В В Timofeeff M N, Lowenstein T K, Da Silva M A M and Harris N B. 2006. Secular vari ation in the major_ion chemistry of seawater: Evidence from fluid inclusions in Cretaceous halitesпј»JпјҪ. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 70: 1977_1994.
В В В В Wang M Q, Zhao Y J, Liu C L and Ding T. 2015. Paleotemperature and significance of the evaporated seawater in salt_forming process of the forth member of Jialin gjiang Formation in the eastern Sichuan Basinпј»JпјҪ. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31( 9): 2745_2750(in Chinese with English abstract).
В В В В Yang J G. 1994. The preliminary study of fluid inclusion in salt from five halit e deposits of four Provinces in southeast Chinaпј»JпјҪ. Journal of Salt Lake Scien ce, 2(3): 1_9 (in Chinese with English abstract).
В В В В Yuan J Q, Cai K Q, Xiao R G and Chen H Q. 1991. The characteristics and genesis of inclusions in salt from Mengyejing potash deposit in Yunnan Provinceпј»JпјҪ. Ea rt h Science_Journal of China University of Geosciences, 16(2): 137_142 (in Chinese with English abstract).
В В В В Zhang Y Q, Dong S W, Li J H and Shi W. 2011. Mesozoic multi_directional compress ional tectonics and formation_reformation of Sichuan basinпј»JпјҪ. Geology in Chin a, 38(2)пјҡ233_250 (in Chinese with English abstract).
В В В В Zhao Y J, Liu C L, Zhang HпјҢLi Z Q, Ding T and Wang M Q. 2015. The controls of p aleotemperature on potassium salt precipitation in ancient salt lakesпј»JпјҪ. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(9): 2751_2756(in Chinese with English abstract).
В В В В Zheng J P, Griffin W L, O Reilly S Y, Zhang M, Pearson N and Pan Y M. 2006. Wide spread Archean basement beneath the Yangtze cratonпј»JпјҪ. Geology, 34(6): 417_420 .В
В В В В
В В В В йҷ„дёӯж–ҮеҸӮиҖғж–ҮзҢ®
В В В В
В В В В и”Ўе…ӢеӢӨпјҢиўҒи§ҒйҪҗ.1986.еӣӣе·қдёүеҸ зі»й’ҫзӣҗжҲҗзҹҝжқЎд»¶е’Ңжүҫзҹҝж–№еҗ‘пј»JпјҪ. еҢ–е·Ҙзҹҝдә§ең°иҙЁ, 8(2): 4_12.
В В В В йҷҲйғҒеҚҺ.1983пјҺй»„жө·жө·ж°ҙ25в„ғзӯүжё©и’ёеҸ‘ж—¶зҡ„жһҗзӣҗеәҸеҲ—еҸҠжҹҗдәӣеҫ®йҮҸе…ғзҙ зҡ„еҲҶеёғ规еҫӢпј»JпјҪ. ең°иҙЁ еӯҰжҠҘпјҢ(4): 379_390пјҺ
В В В В иғЎжҳҺжңҲпјҢдҪ•зәўи“јпјҢи©№з§ҖжҳҘпјҢжЁҠе…ҙж¶ӣ, зҺӢе№ҝ, иҙҫжіҪиҚЈпјҺ2008пјҺеҹәдҪ“еҪ’дёҖе®ҡйҮҸжҠҖжңҜеңЁжҝҖе…үзғ§иҡҖ_ зӯүзҰ»еӯҗдҪ“иҙЁи°ұжі•й”ҶзҹіеҺҹдҪҚеӨҡе…ғзҙ еҲҶжһҗдёӯзҡ„еә”з”Ёпј»JпјҪпјҺ еҲҶжһҗеҢ–еӯҰпјҢ36(7): 947_953.
В В В В иғЎеңЈиҷ№пјҢиғЎе…ҶеҲқпјҢеҲҳеӢҮиғңпјҢзҪ—еҪҰпјҢжһ—е®ҲйәҹпјҢй«ҳеұұпјҺ2001пјҺеҚ•дёӘжөҒдҪ“еҢ…иЈ№дҪ“е…ғзҙ еҢ–еӯҰз»„жҲҗеҲҶжһҗ ж–°жҠҖжңҜвҖ”вҖ”жҝҖе…үеүҘиҡҖз”өж„ҹиҖҰеҗҲзӯүзҰ»еӯҗдҪ“иҙЁи°ұ(LA_ICP_MS) пј»JпјҪпјҺең°еӯҰеүҚзјҳпјҢ8(4): 434_440 пјҺ
В В В В й»„е»әеӣҪ.1998. дёӯеӣҪдёүеҸ зәӘй’ҫзӣҗжІүз§ҜвҖ”вҖ”д»Ҙеӣӣе·қдёәдҫӢпј»JпјҪ.еІ©зӣёеҸӨең°зҗҶпјҢ18(4):23_43.В
В В В В жқҺдәҡж–ҮпјҢи”Ўе…ӢеӢӨпјҢйҹ©и”ҡз”°. 1998. еӣӣе·қзӣҶең°дёүеҸ зі»и’ёеҸ‘еІ©зҡ„еҸҳиҙЁдҪңз”ЁдёҺеҜҢй’ҫеҚӨж°ҙзҡ„жҲҗеӣ пј»J пјҪ. зҺ°д»Јең°иҙЁпјҢ12пјҲ2пјүпјҡ 222_228.
В В В В жһ—иҖҖеәӯ.1994.и®әеӣӣе·қзӣҶең°жө·зӣёдёүеҸ зі»еҗ«й’ҫжҖ§еҸҠжүҫй’ҫж–№еҗ‘пј»JпјҪ. еӣӣе·қең°иҙЁеӯҰжҠҘ,14(2):111_12 0.
В В В В жһ—иҖҖеәӯ.1995.и®әеӣӣе·қзӣҶең°дёүеҸ зі»зӣҗзұ»еҸҳиҙЁдҪңз”ЁеҸҠжүҫй’ҫж–№еҗ‘пј»JпјҪ. еҢ–е·Ҙзҹҝдә§ең°иҙЁ,17(2):93_1 02.
В В В В жһ—иҖҖеәӯпјҢи®ёзҘ–йң–.2009. и®әзӣҗзұ»дҝқеӯҳжқЎд»¶з ”究еҜ№еӣӣе·қзӣҶең°дёүеҸ зі»жүҫй’ҫе·ҘдҪңзҡ„йҮҚиҰҒжҖ§пј»JпјҪ. зӣҗ ж№–з ”з©¶пјҢ17(1):6_12.
В В В В жһ—иҖҖеәӯпјҢдҪ•йҮ‘жқғпјҢзҺӢз”°дёҒпјҢеҸ¶иҢӮжүҚ. 2002a. еӣӣе·қзӣҶең°дёӯдёүеҸ з»ҹжҲҗйғҪзӣҗзӣҶеҜҢй’ҫеҚӨж°ҙең°зҗғеҢ–еӯҰ зү№еҫҒеҸҠе…¶еӢҳжҹҘејҖеҸ‘еүҚжҷҜз ”з©¶пј»JпјҪ. еҢ–е·Ҙзҹҝдә§ең°иҙЁпјҢ24пјҲ2пјүпјҡ72_84.
В В В В жһ—иҖҖеәӯпјҢйғ‘иҢӮе…Ё. 2002b. и®әеӣӣе·қзӣҶең°дёүеҸ зі»зӣҗзұ»зғӯиһҚж°ҙжә¶еҸҳиҙЁеҜ№жүҫй’ҫж–№еҗ‘зҡ„жҺ§еҲ¶пј»JпјҪ. зӣҗ ж№–з ”з©¶пјҢ10пјҲ1пјүпјҡ8_17.
В В В В еҲҳе…ҙиө·пјҢеҖӘеҹ№пјҢи‘Јжө·иүҜпјҢзҺӢеӨ©еҲҡпјҺ2007пјҺеҶ…йҷҶзӣҗж№–зҹізӣҗжөҒдҪ“еҢ…иЈ№дҪ“еқҮдёҖжё©еәҰжҢҮзӨәж„Ҹд№үзҡ„зҺ°д»Ј иҝҮзЁӢз ”з©¶пј»JпјҪ. еІ©зҹіеӯҰжҠҘпјҢ23(1): 113_116пјҺ
В В В В йҷҶжқҫе№ҙпјҢжқҺжҖҖеқӨпјҢйҷҲеҝ—е®ҸпјҢдәҺжө·еі°пјҢйҮ‘е·ҚпјҢйғӯеқӨдёҖ. 2004. ж–°е…ғеҸӨж—¶жңҹдёӯеӣҪеҸӨеӨ§йҷҶдёҺзҪ—иҝӘе°ј дәҡи¶…еӨ§йҷҶзҡ„е…ізі»пј»JпјҪ. ең°еӯҰеүҚзјҳпјҢ11(2): 515_523.
В В В В еӯҹеҮЎе·ҚпјҢеҲҳжҲҗжһ—пјҢеҖӘеҹ№. 2012. е…ЁзҗғеҸӨжө·ж°ҙеҢ–еӯҰжј”еҢ–дёҺдё–з•Ңдё»иҰҒжө·зӣёй’ҫзӣҗжІүз§Ҝе…ізі»жҡЁдёӯеӣҪжө· зӣёжҲҗй’ҫжҺўи®Ёпј»JпјҪ. еҫ®дҪ“еҸӨз”ҹзү©еӯҰжҠҘ. 29(1): 62_69.
В В В В е®Ӣй№ӨеҪ¬пјҢе®ӢжӯЈе№іпјҢиӮ–з« жЈӢ. 1988. е·қдёңеҢ—е®Јжұүең°еҢәе·қ2 дә•еҜҢй’ҫеҚӨж°ҙзЁіе®ҡеҗҢдҪҚзҙ ең°зҗғеҢ–еӯҰзү№еҫҒ еҸҠжүҫй’ҫж„Ҹд№үпј»JпјҪ. дёӯеӣҪең°иҙЁз§‘еӯҰйҷўзҹҝеәҠең°иҙЁз ”究жүҖжүҖеҲҠ, 1: 51_67.
В В В В жұӘжҳҺжіүпјҢиөөиүіеҶӣпјҢеҲҳжҲҗжһ—пјҢдёҒе©·. 2015. еӣӣе·қзӣҶең°дёңйғЁдёүеҸ зі»еҳүйҷөжұҹз»„жҲҗзӣҗжңҹжө“зј©жө·ж°ҙеҸӨжё© еәҰеҸҠе…¶ж„Ҹд№үпј»JпјҪ. еІ©зҹіеӯҰжҠҘпјҢ31пјҲ9пјүпјҡ2745_2750.
В В В В жқЁеҗүж №пјҺ1994пјҺ жҲ‘еӣҪдёңеҚ—еӣӣзңҒдә”дёӘеІ©зӣҗзҹҝеәҠзҹізӣҗдёӯжөҒдҪ“еҢ…иЈ№дҪ“зҡ„еҲқжӯҘз ”з©¶пј»JпјҪпјҺзӣҗж№–з ”з©¶ пјҢ2(3): 1_9пјҺ
В В В В иўҒи§ҒйҪҗпјҢи”Ўе…ӢеӢӨпјҢиӮ–иҚЈйҳҒпјҢйҷҲеҚүжіүпјҺ1991пјҺдә‘еҚ—еӢҗйҮҺдә•й’ҫзӣҗзҹҝеәҠзҹізӣҗдёӯеҢ…иЈ№дҪ“зү№еҫҒеҸҠе…¶жҲҗеӣ зҡ„и®Ёи®әпј»JпјҪ. ең°зҗғ科еӯҰпјҢ16(2):137_142пјҺ
В В В В еј еІіжЎҘпјҢи‘Јж ‘ж–ҮпјҢжқҺе»әеҚҺпјҢж–ҪзӮң. 2011. дёӯз”ҹд»ЈеӨҡеҗ‘жҢӨеҺӢжһ„йҖ дҪңз”ЁдёҺеӣӣе·қзӣҶең°зҡ„еҪўжҲҗе’Ңж”№йҖ пј»JпјҪ.дёӯеӣҪең°иҙЁпјҢ38(2)пјҡ233_250.
В В В В иөөиүіеҶӣпјҢ еҲҳжҲҗжһ—пјҢ еј еҚҺпјҢ LI Z QпјҢ дёҒе©·пјҢ жұӘжҳҺжіү. 2015. еҸӨзӣҗж№–еҚӨж°ҙжё©еәҰеҜ№й’ҫзӣҗжІүз§Ҝ зҡ„жҺ§еҲ¶дҪңз”ЁжҺўи®Ёпј»JпјҪ. еІ©зҹіеӯҰжҠҘпјҢ 31(9): 2751_2756.
 еӯҷе°Ҹиҷ№,иғЎе®ҮйЈһ,еҲҳжҲҗжһ—,дёҒе©·,иғЎжҳҺжңҲ,иөөиүіеҶӣ,жұӘжҳҺжіү.2016.еӣӣе·қзӣҶең°дёүеҸ зәӘеҸӨзӣҗж№–е·Іиҫҫй’ҫзҹізӣҗжһҗеҮәйҳ¶ж®өвҖ”вҖ”жқҘиҮӘзҹізӣҗжөҒдҪ“еҢ…иЈ№дҪ“еҢ–еӯҰз»„жҲҗзҡ„зәҰжқҹ[J].зҹҝеәҠең°иҙЁ,35(6):1157~1168
еӯҷе°Ҹиҷ№,иғЎе®ҮйЈһ,еҲҳжҲҗжһ—,дёҒе©·,иғЎжҳҺжңҲ,иөөиүіеҶӣ,жұӘжҳҺжіү.2016.еӣӣе·қзӣҶең°дёүеҸ зәӘеҸӨзӣҗж№–е·Іиҫҫй’ҫзҹізӣҗжһҗеҮәйҳ¶ж®өвҖ”вҖ”жқҘиҮӘзҹізӣҗжөҒдҪ“еҢ…иЈ№дҪ“еҢ–еӯҰз»„жҲҗзҡ„зәҰжқҹ[J].зҹҝеәҠең°иҙЁ,35(6):1157~1168